Introduction
Israel’s relationship with the Middle East is a topic steeped in history, geopolitics, and conflict. Situated in a region marked by cultural, religious, and political diversity, Israel’s position has been a source of both diplomatic efforts and challenges. This article explores the multifaceted dynamics of Israel’s relations with the Middle East, its neighbors, and the broader region.
Historical Background: Israel’s Relationship With the Middle East
The history of Israel’s relationship with the Middle East is characterized by a complex interplay of historical events, conflict, and shifting alliances. The establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 marked a turning point in the region, leading to tensions, wars, and peace processes.
- Arab-Israeli Conflict: The Arab-Israeli conflict, rooted in territorial disputes and opposing national aspirations, has been a defining factor in the region. Wars in 1948, 1967, and 1973 have shaped the geopolitical landscape.
- Peace Agreements: Israel has made significant strides in achieving peace with some of its neighbors. The Camp David Accords with Egypt in 1978 and the peace treaty with Jordan in 1994 are notable examples.
- Palestinian Conflict: The Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains a central issue. The Oslo Accords in the 1990s aimed at resolving the conflict but have seen limited success, leading to ongoing tensions.
ALSO READ :A Complex History: Israel, Gaza, And Palestine Relations
Geostrategic Position
Israel’s geographic location in the Middle East is of paramount importance. It is situated at the crossroads of Africa and Asia, with access to the Mediterranean Sea. This strategic location has shaped its foreign policy, defense strategies, and regional interactions.
- Security Concerns: Israel’s national security is a driving force in its foreign policy. The country has faced security challenges from militant groups and hostile neighbors, influencing its stance on issues such as borders and the establishment of a demilitarized Palestinian state.
- Regional Alliances: Israel has developed strategic alliances with nations outside the Middle East, including the United States. These alliances provide diplomatic support, military aid, and economic partnerships.
- Energy and Water Resources: Israel’s efforts to secure energy resources, such as natural gas, and manage water resources are important aspects of its regional policy. These factors contribute to its relationships with neighboring countries.

Diplomatic Efforts
Israel’s diplomacy in the Middle East spans a spectrum of engagement, from bilateral relations to multilateral organizations. Several diplomatic efforts have aimed at addressing regional issues and conflicts:
- Middle East Peace Process: The pursuit of a two-state solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict has been a central theme in Israeli diplomacy. This includes negotiations and agreements, such as the Oslo Accords and the Roadmap for Peace.
- Regional Stability: Israel has a vested interest in regional stability. It seeks to counter common threats, such as terrorism and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, through cooperation with its neighbors and regional actors.
- Economic Partnerships: Economic cooperation and trade relations play a role in diplomacy. These interactions include collaboration with countries like Jordan and Egypt in areas such as energy and technology.
Challenges and Opportunities
Israel’s relationships with its Middle Eastern neighbors are marked by both challenges and opportunities. The region is characterized by fluidity, with shifting alliances and the potential for conflict resolution.
- Challenges: Persistent conflict, religious tensions, and historical grievances continue to present challenges. The unresolved Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains a key issue.
- Opportunities: Diplomatic openings and shared interests in areas such as security, technology, and energy present opportunities for cooperation and reconciliation.
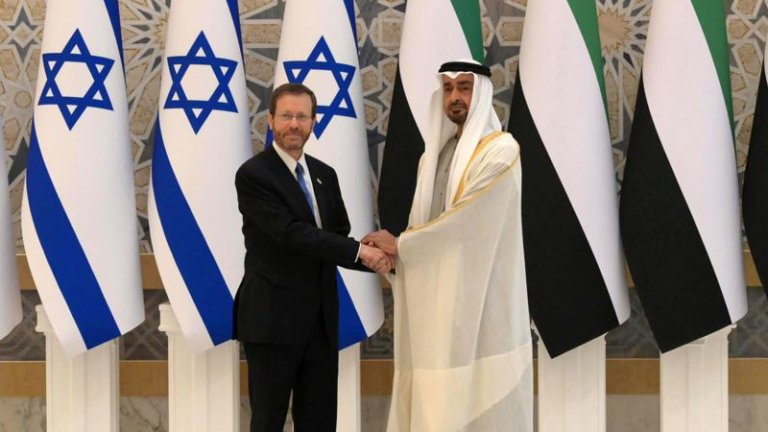
- Normalization Agreements: The Abraham Accords in 2020 signaled a historic shift in Middle Eastern diplomacy. Israel’s normalization agreements with the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain opened new doors for regional collaboration.

Conclusion
Israel’s relationship with the Middle East is a complex and evolving story that encompasses historical conflicts, strategic alliances, and diplomatic efforts. The region’s multifaceted dynamics, marked by longstanding disputes and changing political landscapes, continue to shape Israel’s position. As the Middle East faces ongoing challenges and opportunities, the prospects for peace, stability, and cooperation in the region will remain topics of global importance.
ALSO READ: Strengthening Ties: The Bilateral Relationship Between India And Israel




































