Introduction
The history of Israel is a remarkable and multifaceted narrative that has left a profound impact on the world. From its ancient roots to the establishment of the modern state of Israel, this article will take you on a journey through time, tracing the key events and developments that have shaped this nation’s history.
Ancient Roots: The History Of Israel
The history of Israel can be traced back thousands of years. In antiquity, the region known today as Israel was home to various ancient civilizations, including the Canaanites, Philistines, and Hebrews. It was a crossroads for trade and cultural exchange.
- Ancient Israelites: The Hebrews, who would become the Israelites, emerged as a distinct people. They are central figures in the Old Testament of the Bible. The story of their exodus from Egypt and the giving of the Ten Commandments at Mount Sinai are foundational elements of their history.
- Kingdom of Israel: The United Kingdom of Israel, under King David and his son Solomon, reached its zenith around the 10th century BCE. The First Temple in Jerusalem was constructed during this period.
- Babylonian Exile: In 586 BCE, the Babylonians captured Jerusalem and destroyed the First Temple. Many Israelites were exiled to Babylon, a significant event in Jewish history.
The History Of Israel
Roman and Byzantine Periods
- Roman Rule: Israel came under Roman control in the 1st century BCE. The city of Jerusalem was destroyed in 70 CE, and the Second Temple was razed. The Jewish diaspora began as a result.
- Byzantine Rule: After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire, known as the Byzantine Empire, maintained control over the region.
ALSO READ : Navigating Complex Waters: Israel’s Relationship With The Middle East
Islamic Caliphates and Crusades
- Islamic Conquest: In the 7th century CE, Islamic armies conquered the region, and Jerusalem became a significant city in the Islamic world.
- Crusader Period: The First Crusade in 1099 saw the establishment of Crusader states in the region, including the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
Ottoman Empire
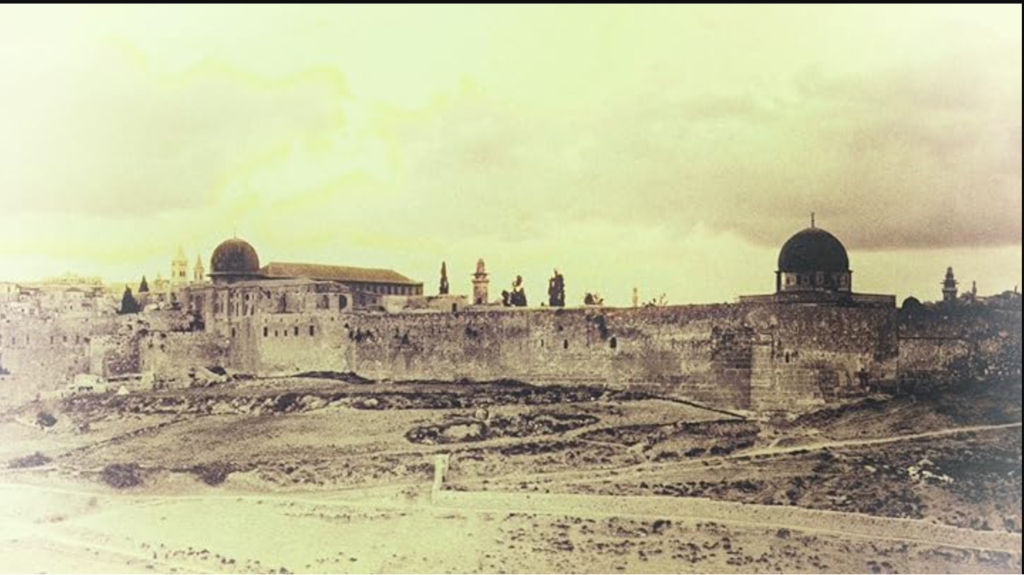

The History Of Israel
- Ottoman Rule: The Ottoman Empire took control of the area in the 16th century and ruled for several centuries. The population consisted of Jews, Christians, and Muslims.
British Mandate and Modern Israel
- British Mandate: After World War I, the League of Nations granted Britain a mandate over Palestine. Tensions between Jewish and Arab communities grew during this period.
- Partition Plan (1947): The United Nations proposed a partition plan that would create separate Jewish and Arab states in Palestine. The plan was accepted by Jewish leaders but rejected by Arab leaders, leading to the Arab-Israeli War in 1948.
- Israeli Independence: On May 14, 1948, David Ben-Gurion, Israel’s first Prime Minister, declared the establishment of the State of Israel. This declaration was followed by a conflict with neighboring Arab states.
Arab-Israeli Conflicts
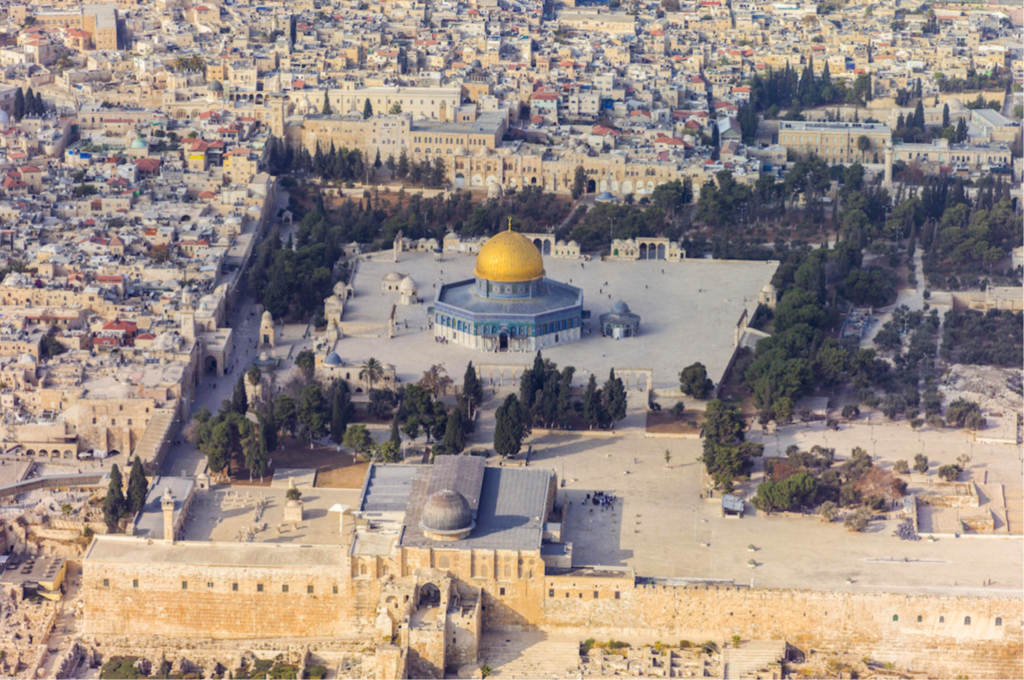

The History Of Israel
- War of Independence (1948-1949): The War of Independence saw Israel fighting against neighboring Arab states and resulted in armistice agreements.
- Suez Crisis (1956): Israel, along with France and the United Kingdom, engaged in military operations against Egypt during the Suez Crisis.
- Six-Day War (1967): In 1967, Israel waged a brief but decisive war against Egypt, Jordan, and Syria, capturing the Gaza Strip, West Bank, and East Jerusalem, among other territories.
- Yom Kippur War (1973): The Yom Kippur War, also known as the October War, was a surprise attack on Israel by Egypt and Syria. It had a significant impact on regional politics.
Peace Agreements and Contemporary Challenges
- Camp David Accords (1978): Egypt became the first Arab country to recognize Israel, leading to a peace treaty under the Camp David Accords.
- Oslo Accords (1993): The Oslo Accords were a series of agreements between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), aimed at achieving peace and self-determination for the Palestinian people.
- Contemporary Challenges: The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, ongoing disputes over territory, security concerns, and the status of Jerusalem are central issues in the region.
The Modern State of Israel

The History Of Israel
- Birth of a Nation: The establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 was a defining moment in the history of the region. After centuries of exile, the Jewish people regained a homeland. Israel’s founders were committed to creating a democratic and inclusive state.
- Immigration and Growth: Following its establishment, Israel experienced waves of immigration, particularly of Jewish survivors of the Holocaust and Jews from Arab countries. This influx of diverse cultures and experiences shaped the nation’s identity.
- Arab-Israeli Conflict: The Israeli-Arab conflict persisted in the post-independence era, with tensions and wars such as the Six-Day War (1967) and the Yom Kippur War (1973). Efforts to achieve peace, such as the Camp David Accords with Egypt and the Oslo Accords with the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), have marked significant moments in Israel’s history.
- Territorial Disputes: Israel’s control of territories like the West Bank and Gaza Strip has been a source of ongoing tension and disputes. The construction of settlements in these areas has further complicated the conflict.
Modern Challenges and Achievements

The History Of Israel
- Peace Process: The Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains a central challenge. Negotiations, peace agreements, and diplomatic efforts have seen progress and setbacks, with the goal of a two-state solution still being pursued.
- Economic and Technological Advancements: Israel has experienced significant economic growth and technological advancements. It is known for its innovation in fields like cybersecurity, agriculture, and medical research.
- Diverse Society: Israel’s population is diverse, with Jews, Arabs, Druze, and other communities living side by side. This diversity has enriched the nation’s cultural fabric but also presents social and political challenges.
- Security Concerns: Israel faces ongoing security concerns, including regional conflicts, terrorism, and threats from non-state actors. The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) plays a pivotal role in ensuring national security.
- Diplomacy: Israel has cultivated diplomatic relations with various countries, particularly the United States. In recent years, it has seen normalization agreements with some Arab nations, marking a significant shift in regional dynamics.
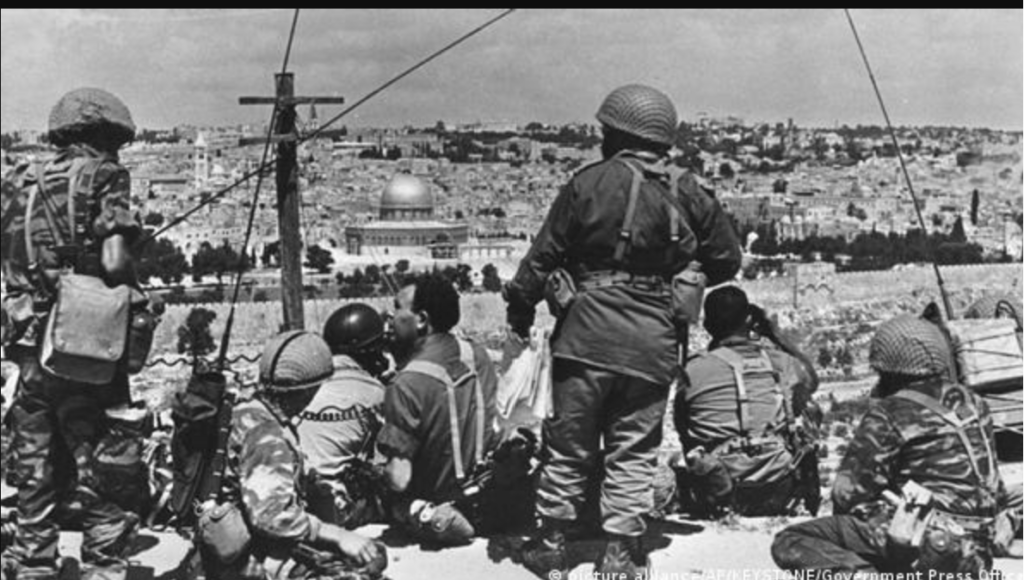

The History Of Israel
Conclusion
The history of Israel is a story of resilience, determination, and complex challenges. From ancient roots to modern statehood, Israel’s journey has been marked by wars, peace agreements, and an ongoing quest for a peaceful resolution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. As a nation of cultural, technological, and historical significance, Israel’s role in the Middle East continues to evolve, reflecting the dynamism and complexities of the region. Understanding its rich history is integral to comprehending its place in the world and its aspirations for the future.
ALSO READ ; Understanding The Differences Between Hamas And Palestine




































