Introduction
Charles Darwin’s The theory of evolution by natural selection is one of the most profound and revolutionary concepts in the history of science. At the heart of this theory is the work of Charles Darwin, a British naturalist, and biologist. Darwin’s groundbreaking ideas, which he detailed in his 1859 book “On the Origin of Species,” laid the foundation for our modern understanding of how life on Earth has evolved over billions of years. In this article, we will explore Charles Darwin’s life, the concept of natural selection, and its enduring impact on biology and our understanding of the natural world.
Charles Darwin: A Naturalist’s Journey

- Early Life: Charles Robert Darwin was born on February 12, 1809, in Shrewsbury, England. He was the fifth of six children in a well-to-do and intellectually curious family. His father, Robert Darwin, was a physician, and his grandfather, Erasmus Darwin, was a noted physician, poet, and philosopher.
- Educational Background: Darwin initially attended medical school at the University of Edinburgh but found the dissection of animals more intriguing than the study of medicine. He later studied theology at the University of Cambridge, where he became influenced by naturalist John Stevens Henslow.
- The Voyage of the Beagle: In 1831, at the age of 22, Darwin embarked on a five-year scientific expedition aboard the HMS Beagle. This journey took him around the world and provided him with invaluable opportunities to observe the natural world. His experiences and observations during this voyage profoundly influenced his scientific thinking.
Also read : Facts About Aurora Borealis: How The Northern Lights Operate
The Concept of Natural Selection
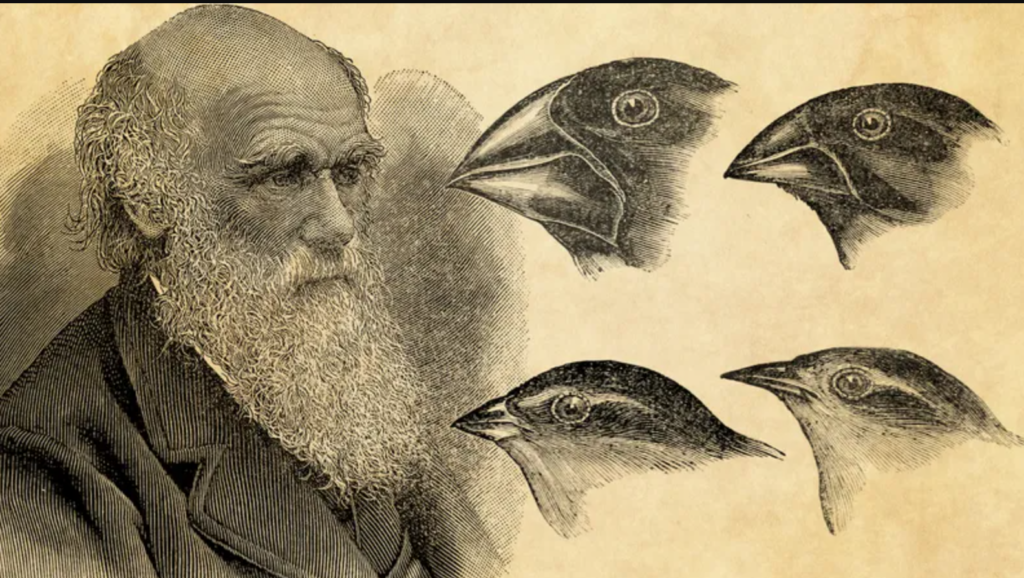

- Observations in Nature: During his travels, Darwin meticulously observed and collected specimens of plants and animals. He noted the remarkable diversity of life and the adaptations of organisms to their environments.
- The Mechanism of Evolution: Upon his return to England in 1836, Darwin began to formulate his theory of natural selection. He proposed that species evolved through a process in which those individuals with advantageous traits (adaptations) would be more likely to survive and reproduce. Over time, these advantageous traits would become more common in the population.
- Publication of “On the Origin of Species”: After years of research and refinement of his ideas, Charles Darwin published “On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection” in 1859. The book presented his theory of evolution and natural selection. It was met with both acclaim and controversy.
Enduring Impact and Legacy
Charles Darwin’s theory of natural selection has left a profound and lasting impact on science and our understanding of the natural world. Here are some key aspects of his legacy:
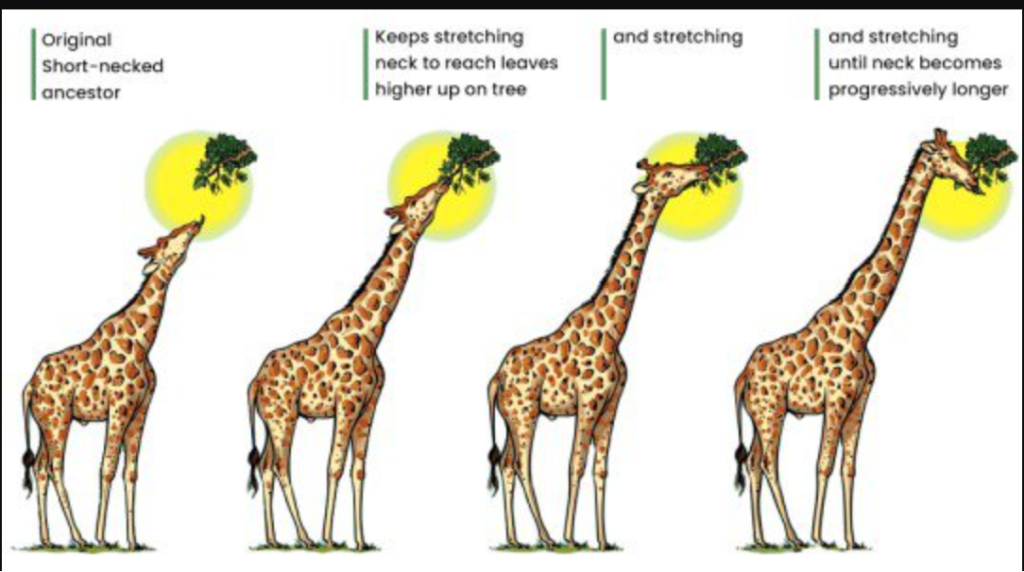
- Unifying Biology: Darwin’s theory provided a unifying framework for biology. It explained the diversity of life and connected seemingly unrelated fields, such as paleontology, embryology, and comparative anatomy.
- Evidence from Multiple Disciplines: Subsequent research has provided a wealth of evidence supporting natural selection, including the fossil record, comparative anatomy, genetics, and the observed adaptations in living organisms.
- Continual Relevance: More than a century and a half after the publication of “On the Origin of Species,” Darwin’s theory remains central to the study of biology and continues to guide scientific investigations.
- Cultural and Philosophical Impact: Darwin’s work challenged prevailing cultural and religious beliefs about the origins of life and the natural world, sparking debates that continue to this day.
Ongoing Discoveries and Revisions
Darwin’s theory of natural selection provided a revolutionary framework for understanding the evolution of species, but it was just the beginning. Subsequent generations of scientists have built upon his work and made significant advancements in the field of evolutionary biology.

- Genetics and Heredity: One of the most significant developments following Darwin’s time was the discovery of the role of genetics in evolution. Gregor Mendel’s work on the inheritance of traits provided a mechanism for understanding how variations are passed from one generation to the next. The merging of Mendelian genetics with Darwin’s theory led to the modern synthesis of evolutionary biology, which strengthened the understanding of how natural selection operates at the genetic level.
- Fossil Record: Ongoing paleontological research has provided a wealth of fossil evidence that supports and refines our understanding of evolutionary processes. The discovery of transitional fossils, such as Tiktaalik, Archaeopteryx, and Ambulocetus, has illuminated the gradual transformations that have occurred in various lineages over time.
- Molecular Biology: The advent of molecular biology and DNA sequencing has allowed scientists to explore the genetic relationships among species. Comparative genomics and the study of molecular clocks have provided insights into the timing of evolutionary events and the relationships between different organisms.
Challenges to Darwin’s Theory
While Darwin’s theory of natural selection has been overwhelmingly supported by scientific evidence, it has not been without its challenges. Some of the key debates and questions in the field of evolutionary biology include:
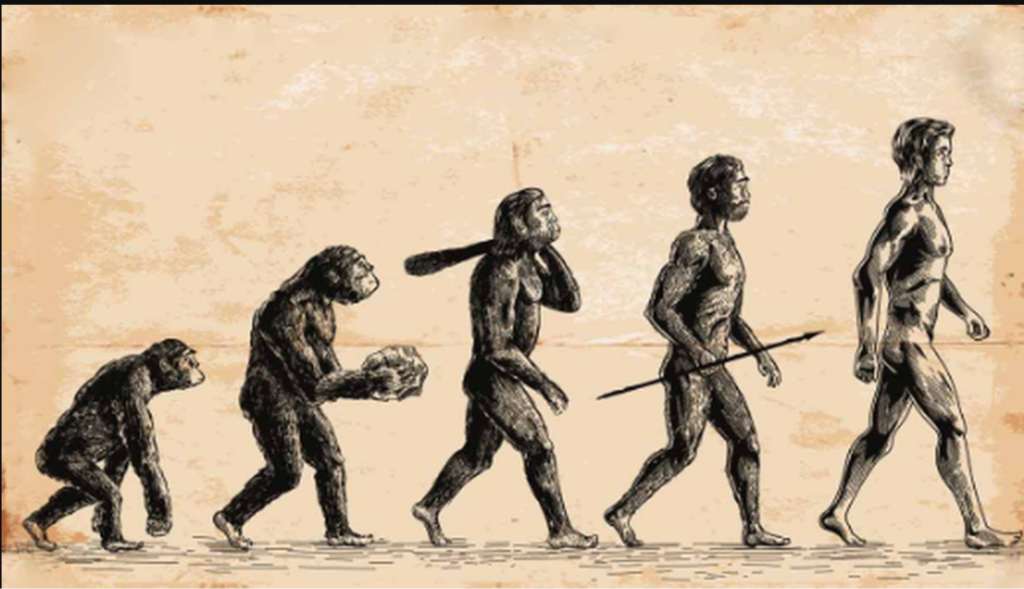

- The Mechanism of Speciation: Scientists continue to study the mechanisms by which new species arise. While natural selection is a driving force in adaptation, other processes such as genetic drift, sexual selection, and hybridization also play essential roles in speciation.
- The Origin of Life: While Darwin’s theory addresses the diversity and adaptation of life, it does not address the origin of life itself. The field of abiogenesis seeks to understand how life may have emerged from non-living matter.
- Microevolution vs. Macroevolution: Some debates revolve around the distinction between microevolution (changes within species) and macroevolution (the origin of new species and higher taxa). Understanding the factors that lead to the emergence of entirely new species is an ongoing area of research.
Darwin’s Legacy in the 21st Century
Charles Darwin’s work has proven to be one of the most enduring and influential contributions to science. In the 21st century, the legacy of his ideas continues to shape our understanding of the natural world and informs countless fields of science, from biology to paleontology, genetics, and anthropology.
Darwin’s emphasis on empirical observation, the meticulous study of natural phenomena, and the formulation of testable hypotheses remains a model for scientific inquiry. As we continue to explore the complexity of life on Earth and its history, we owe a debt of gratitude to Charles Darwin, whose intellectual courage and groundbreaking insights have forever changed our perception of the natural world. His theory of natural selection remains a testament to the power of science to illuminate the mysteries of life.
Also read : Ozone Layer: A Hole In The Earth’s Protective Shield




































