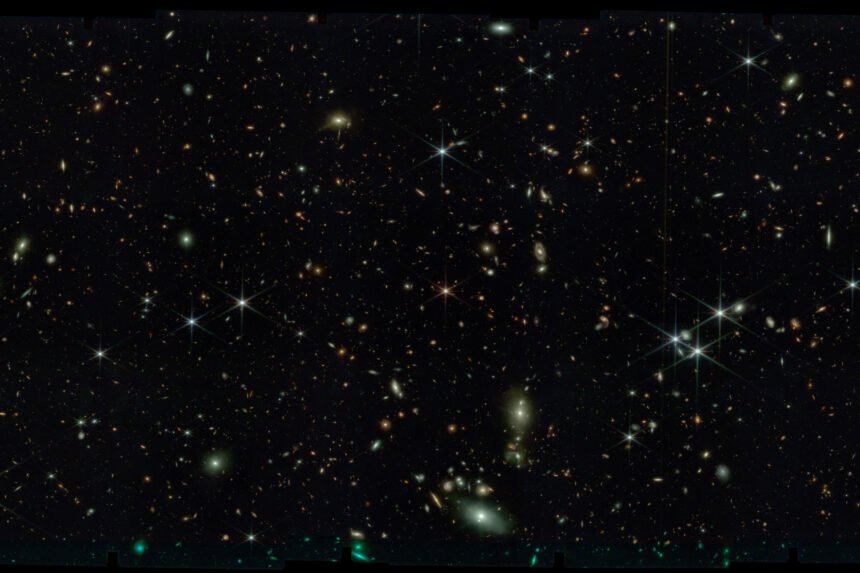
Introduction
Space, the vast expanse that envelopes our planet and extends far beyond our imagination, is often described as a vacuum, a place of emptiness. Yet, it is not truly empty. In this article, we will explore the nature of space, what keeps it seemingly empty, and the subtle but fascinating components that make up the interstellar void.
The Illusion of Emptiness
When we gaze into the night sky, space appears as a vast, black void, seemingly devoid of matter. However, this perception is deceiving. Space is far from empty; it is simply incredibly sparse. The vacuum of space is not a complete void but is filled with minute quantities of matter and energy.
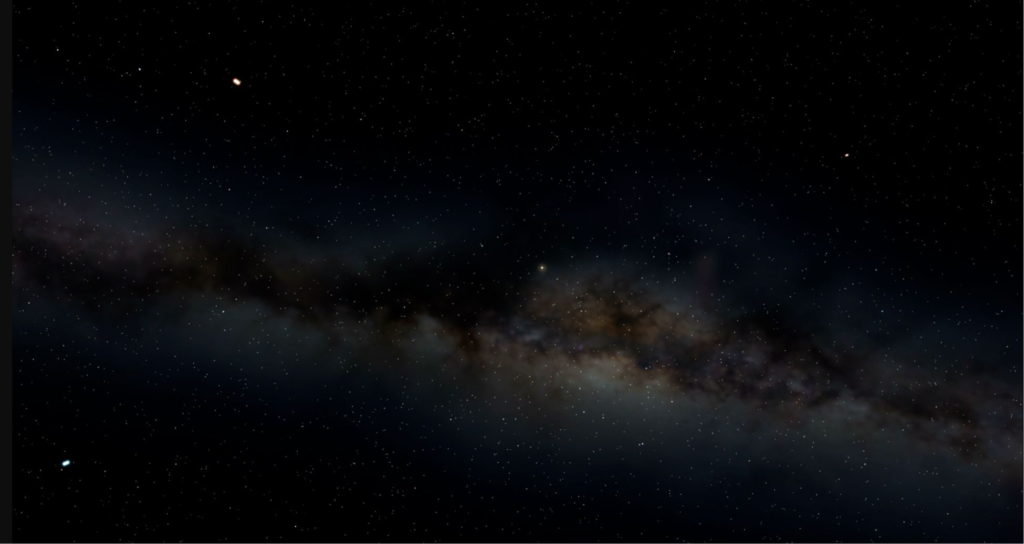

The Vacuum of Space
Space is not a perfect vacuum, but it comes close. In the regions of space between celestial bodies, such as stars, planets, and galaxies, there are only a few atoms and molecules per cubic centimeter. This extreme rarity of matter makes space seem empty when compared to the dense environment of our planet.
Cosmic Dust
One of the components that fills space is cosmic dust. These microscopic particles, composed of various materials, including silicates, carbon, and ices, are scattered throughout the cosmos. They are remnants of ancient stars, and while they are sparse, their sheer numbers mean that they play a crucial role in the formation of stars and planets.
Gas in the Interstellar Medium
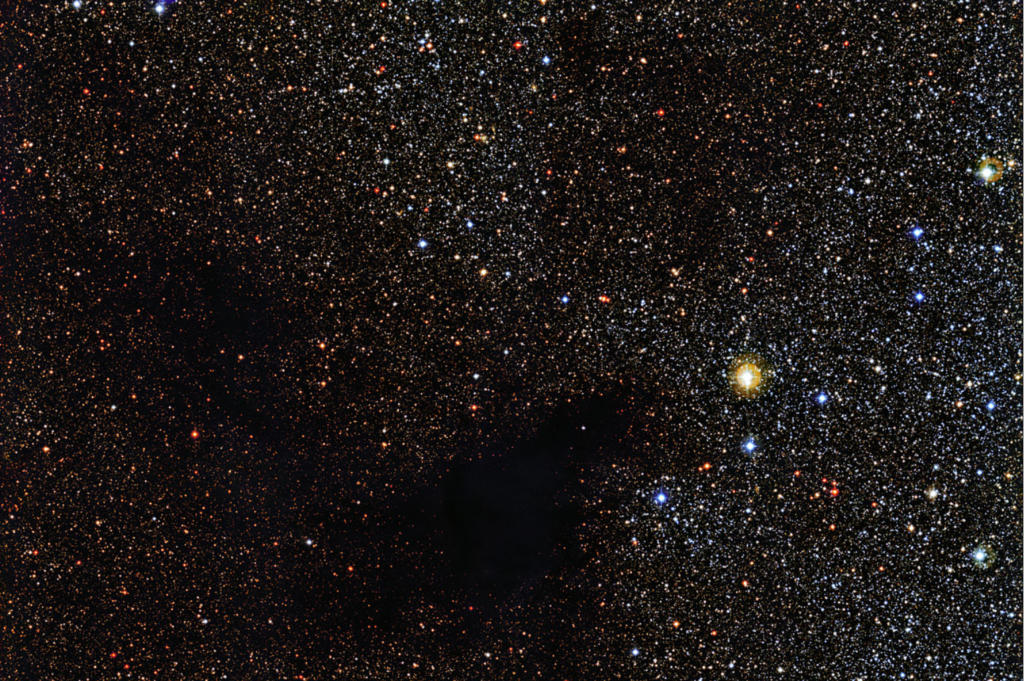

Interstellar space contains extremely diffuse clouds of gas. These clouds consist of hydrogen and helium, the two lightest elements in the universe. While the density of gas in these clouds is incredibly low, it is not negligible. These clouds are the birthplaces of stars, where gravitational forces cause them to condense and ignite nuclear fusion.
Dark Matter and Dark Energy
While the matter we can see, such as stars, planets, and gas clouds, makes up only a small fraction of the universe’s content, dark matter and dark energy are believed to constitute the majority. Dark matter is a mysterious, invisible substance that exerts gravitational forces, holding galaxies together. Dark energy, on the other hand, is a force that is causing the universe’s expansion to accelerate. These enigmatic components of the universe are key players in the cosmic landscape.

The Absence of Air
One of the reasons space appears empty is the absence of air, which is essential for our human senses. Space is a vacuum because it lacks the gases we breathe on Earth. This absence of air allows for the almost instantaneous dissipation of sound and the prevention of most chemical reactions, contributing to the perception of emptiness.
Radiation in Space
Space is not just filled with matter; it also contains radiation. Cosmic background radiation, a remnant of the Big Bang, permeates the universe. Additionally, electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, X-rays, and radio waves, travels through space, allowing us to observe distant galaxies and celestial objects.
The Expanding Universe

One of the most remarkable features of space is its vastness, which extends infinitely beyond the confines of our Solar System. Space itself is not stationary; it is constantly expanding. This phenomenon was first discovered by astronomer Edwin Hubble in the early 20th century and has since become a fundamental principle of cosmology.
As the universe expands, galaxies move away from each other, and the space between them grows. The expanding nature of space, combined with the influence of dark energy, results in the observed acceleration of this expansion.
Cosmic Background Radiation
Space, though sparse, is not completely devoid of energy. The cosmic microwave background radiation is a crucial component of the universe’s background. This radiation is a faint, almost uniform glow that permeates space and is a relic of the Big Bang. It was discovered by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson in 1964, providing strong evidence for the Big Bang theory.
Interstellar Particles
While the density of particles in space is incredibly low compared to our planet’s surface, space is not entirely devoid of matter. Interstellar particles, including tiny grains of cosmic dust, are sprinkled throughout the universe. These particles can scatter light and affect the colors of starlight as it passes through space.
Magnetic Fields in Space
Space is not just about matter and radiation; it also contains magnetic fields. Magnetic fields play a vital role in shaping the universe, influencing the behavior of charged particles and the formation of stars and galaxies.
The Vacuum of Space

The vacuum of space is not a complete void but rather a dynamic arena filled with matter, energy, radiation, magnetic fields, and the expanding fabric of the universe itself. Our perception of space as empty is a testament to the vast scale and sparse distribution of its components.
Scientific Exploration
Our understanding of space as a dynamic and intricate environment has been greatly advanced through scientific exploration. Telescopes, both ground-based and space-based, have enabled us to peer deep into the cosmos, revealing the hidden wonders of distant galaxies, nebulae, and cosmic phenomena. Space missions, such as those conducted by NASA and other space agencies, have brought us closer to the mysteries of our Solar System and beyond.

In Conclusion
The perception of space as empty is an illusion. Space is not a void but rather a canvas upon which the cosmos paints its grand tapestry. Filled with cosmic dust, interstellar particles, radiation, magnetic fields, and the forces of dark matter and dark energy, space is a testament to the boundless complexity of the universe. Understanding the intricacies of space is an ongoing endeavor that deepens our appreciation for the cosmos and continues to inspire exploration and discovery.
Also read : Black Hole: Are There Different Types Of Black Holes?




































