Fuel is essential for many applications, such as transportation, power generation, and heating. However, fuel also poses significant safety risks, as it can easily catch fire and cause explosions, injuries, and environmental damage. To address this problem, a team of chemical engineers from the University of California, Riverside, has developed a novel liquid fuel that can only ignite when an electric current is applied, making it immune to accidental fires.
The Innovation of the Liquid Fuel
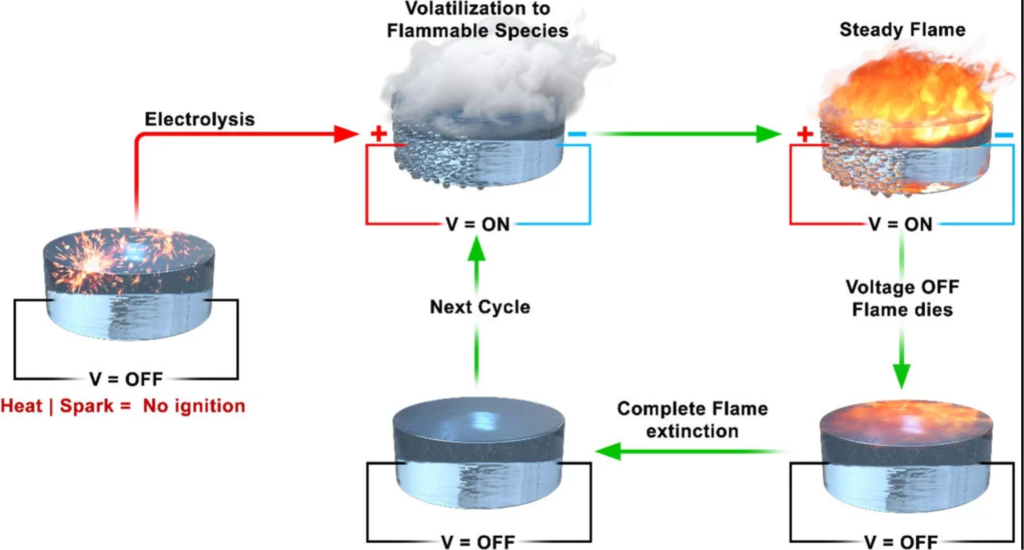
The innovative liquid fuel is based on a type of salt called an ionic liquid, which has a low melting point and does not evaporate. The researchers modified the ionic liquid by replacing some of its atoms with perchlorate, a compound that can release oxygen when heated. The resulting liquid fuel has a unique property: it does not react to flames, but it can produce vapor when an electric current is applied. The vapor can then be ignited by a spark, creating a controlled combustion.
Also read : Storage Choices: Understanding Why Propane Is In Household Tanks, But Natural Gas Is Not

The researchers tested the liquid fuel by attaching a device called a flight-recorder to a glass container filled with the fuel. The device can apply an alternating current (AC) voltage to the fuel and measure its temperature, pressure, and electric current. The researchers found that when the AC voltage was positive, the fuel produced vapor that could be ignited by a lighter. When the AC voltage was negative, the fuel stopped producing vapor and the flame went out. The researchers were able to repeat this process multiple times, demonstrating the switchable and reversible nature of the fuel.

The Implications and Future Prospects
The liquid fuel has several advantages over conventional fuels, such as gasoline and diesel. It is safer to store and transport, as it does not pose fire hazards. It is also more efficient and environmentally friendly, as it does not produce harmful emissions, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. The liquid fuel could potentially revolutionize the safety and performance of various applications, such as vehicles, generators, and rockets.
However, the liquid fuel also faces some challenges and limitations. It is more expensive and complex to produce than conventional fuels. It also requires a special ignition system that can generate electric current and spark. Moreover, it is not compatible with existing engines and fuel systems, which would need to be modified or replaced.
Therefore, the researchers plan to continue their research and development of the liquid fuel, and to explore its feasibility and scalability for practical use. They also hope to collaborate with other experts and industries to optimize the fuel’s properties and applications[1][1].
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Non-Flammable Liquid Fuels
Q: What is the significance of non-flammable liquid fuels?
A: Non-flammable liquid fuels represent a groundbreaking advancement in fuel safety. These fuels are designed to resist ignition under normal circumstances, reducing the risk of accidental fires associated with traditional combustible liquids.
Q: How do scientists create non-flammable liquid fuels?
A: Scientists manipulate the chemical composition of the fuel, introducing elements that significantly raise the temperature required for ignition. This results in a liquid substance that remains inert in the presence of common ignition sources.
Q: What are the advantages of non-flammable liquid fuels for industries?
A: Industries heavily reliant on liquid fuels, such as transportation, manufacturing, and energy production, can benefit from increased safety. Non-flammable fuels reduce the risk of fire-related accidents during storage, transportation, and usage, enhancing workplace safety and operational efficiency.
Q: How do non-flammable liquid fuels impact transportation safety?
A: Non-flammable liquid fuels enhance transportation safety by reducing the risk of fires in the event of accidents or spills. This has implications for both passenger safety and the safety of first responders. Additionally, the stability of these fuels opens possibilities for novel transportation technologies.
Q: What is the environmental impact of non-flammable liquid fuels?
A: The development of non-flammable liquid fuels aligns with environmental sustainability goals. Traditional fuels contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Non-flammable alternatives offer a safer option while addressing environmental concerns.
Q: What challenges do non-flammable liquid fuels face, and how are they being addressed?
A: Challenges include optimizing formulations to balance safety and energy efficiency, as well as addressing scalability and cost-effectiveness for large-scale production. Ongoing research aims to refine the properties of non-flammable liquid fuels for widespread adoption.
Q: How might the introduction of non-flammable liquid fuels impact safety standards?
A: The introduction of non-flammable liquid fuels has the potential to redefine safety standards across industries. Regulatory bodies and safety organizations may need to adapt guidelines to accommodate these innovative fuels, ushering in an era where the risk of flammable liquid-related accidents is significantly reduced.
Q: What is the future outlook for non-flammable liquid fuels?
A: As research and development progress, the applications of non-flammable liquid fuels may extend to unforeseen areas, from emergency power systems to space exploration. The positive impact on workplace safety, environmental sustainability, and technological innovation could mark a transformative era in fuel technology.
Also read : Shedding Light On Radio Antennas: Can They Emit Visible Light?




































