Find out about the various kinds of sexual disorders and dysfunctional conditions, their causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Sexual function is a product of the mind and body. Physical and mental health, not just sex organs, all play a pivotal role. In fact,the brain is often considered the most significant sexual organ. Similarly, the reasons for sexual dysfunction, or any problem that prevents a person or couple from having satisfying sex, can be complex.
It’s normal to have some hiccups between the sheets. But sometimes sexual problems cause individuals or couples enough distress that it rises to the level of sexual dysfunction or a disorder. That’s when it can be especially useful to seek help.
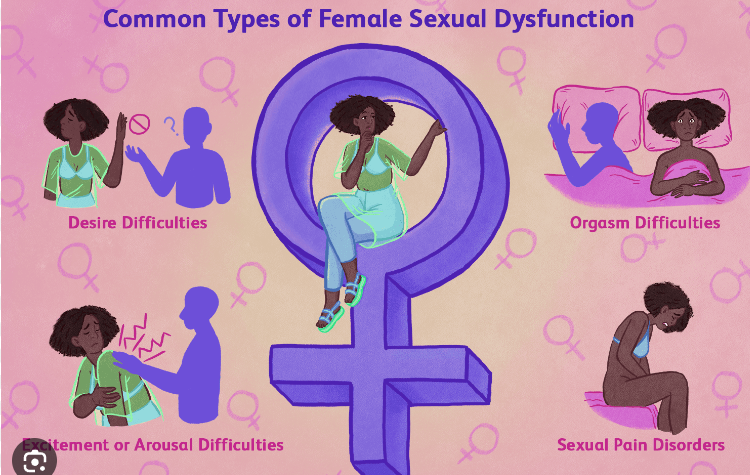
Types of sexual disorders and dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction generally falls into one of four categories:
- Arousal disorders, primarily the inability to become aroused or excited by sexual activity,.
- Desire disorders: having low libido or a lack of sex drive.
- Orgasmic disorders: inability or difficulty having orgasms.
- Painful sex.

Causes of sexual disorders and dysfunction
Just as there are many different sexual disorders, the causes for these vary significantly. Relationship problems or poor communication between partners can be at issue. But a host of underlying general and mental health concerns can also contribute.
Symptoms of sexual disorders and dysfunction
At the most basic level, the signposts pointing to sexual dysfunction highlight just that: difficulty having satisfying sex.
Symptoms may include:
- A lack of sexual desire.
- Trouble becoming aroused.
- Pain during sex.
- Difficulty or inability to achieve orgasm.
For women, symptoms also include:
- Vaginal dryness or lack of lubrication during sex.
- Vaginal spasms or inflammation of the vulva.
For men, symptoms also include:
- Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection sufficient for sex.
- Ejaculation issues: too soon, delayed or inability to ejaculate at all despite stimulation.

Diagnosis of sexual disorders and dysfunction
Typically, issues become apparent to individuals or their partners. Unfortunately, experts say, these problems aren’t frequently shared with doctors. Given the impact on quality of life and the fact that it can sometimes reflect other health issues, it’s important to share your concerns with a professional who has experience addressing sexual dysfunction, such as an OB-GYN, urologist or certified sex therapist. You can start with your primary care doctor, and depending on their expertise in dealing with the sexual health issues you’re facing, request a referral to another professional as needed. Medical professionals and therapists frequently collaborate with physicians in sexual medicine to address the various physical and mental causes of sexual dysfunction.

Often, a physical exam, a health history and a discussion of symptoms are all that’s needed to make a diagnosis. Sometimes, the discovery of sexual dysfunction will trigger a broader evaluation of a person’s underlying health. This can unearth whether varying conditions, from diabetes to depression or treatments, such as certain medications like antidepressants, may be contributing.

Treatments of sexual disorders and dysfunction
There are numerous approaches for treating sexual dysfunction. Everybody tries to deal with the root.
PDE5 inhibitors, such as sildenafil (Viagra), treat blood flow issues that cause erectile dysfunction in males with ED. Nevertheless, underlying medical issues, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease, are not addressed by these drugs. Therefore, it’s critical to control those conditions and adopt heart-healthy, plant-based diets and lifestyle modifications, including weight loss. Such modifications can help prevent ED or even treat mild ED, in addition to improving heart health.
Also read-Sleep Disorders : A Patient’s Guide To Sleep Disorders And Its Symptoms
images source: Google
Disclaimer: The opinions and suggestions expressed in this article are solely those of the individual analysts. These are not the opinions of HNN. For more, please consult with your doctor




































