The Bab al Mandeb’s location on one of the world’s busiest shipping routes makes it a global flashpoint. Here’s what you should know about its past and present.
The Bab al Mandeb : Introduction
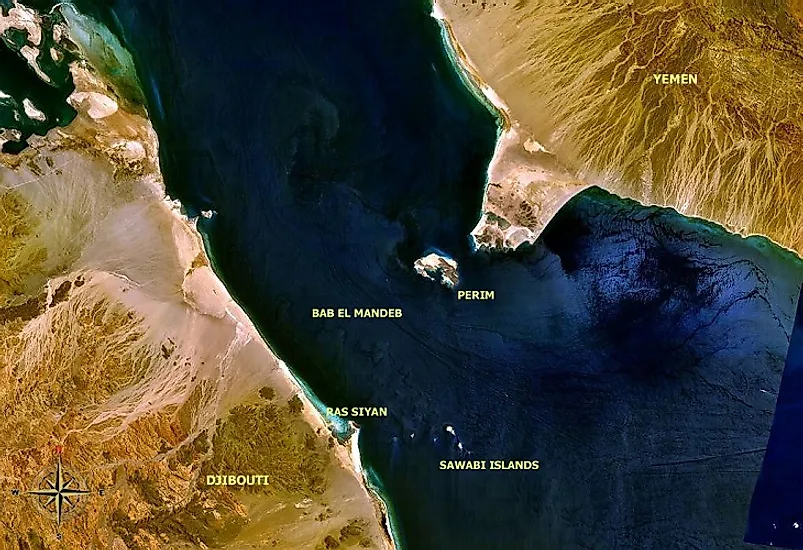
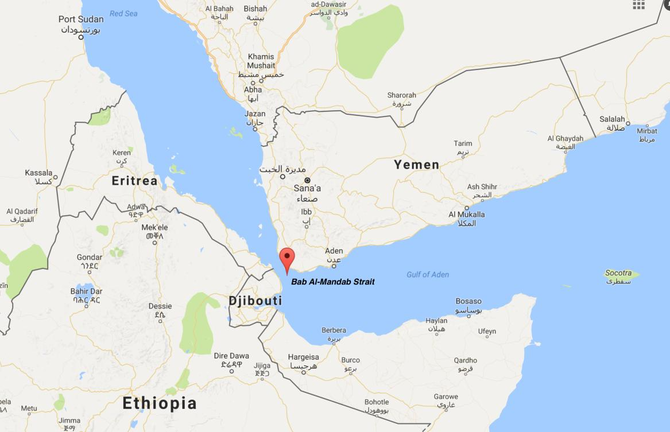
The Bab al Mandeb, a relatively small strait located between the Horn of Africa and the Arabian Peninsula, has recently captured global attention due to its strategic significance in world affairs. Serving as a crucial link between the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea via the Suez Canal, the Bab al Mandeb has become a focal point in recent headlines, primarily due to drone attacks on commercial shipping by Yemen-based Houthi forces. In this article, we delve into the history, current developments, and the global importance of this narrow waterway.
ALSO READ : The Arabian Sea : A Maritime Gateway And Ecological Treasure
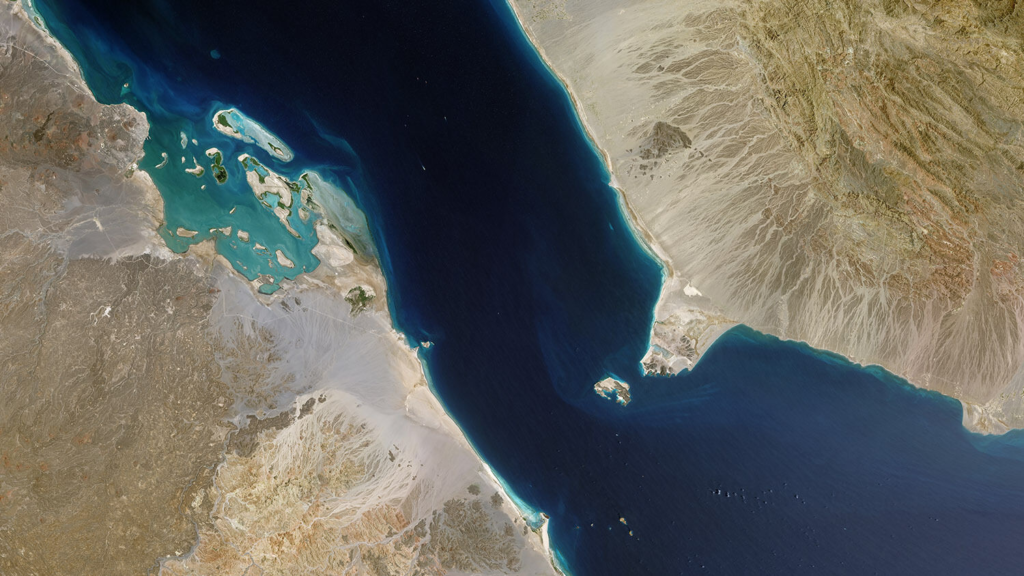

Geography and name
Stretching 20 miles wide and 70 miles long, the Bab al Mandeb forms the southern entrance to the Red Sea from the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean. Eritrea and Djibouti border it to the west, while Yemen lies on its eastern edge. The name “Bab al Mandeb” translates to “Gate of Tears” or “Gate of Grief” in Arabic, reflecting the historical perils of navigating its narrow waters plagued by crosscurrents, unpredictable winds, reefs, and shoals.
Current headlines
Recent drone attacks on commercial shipping by Yemen-based Houthi forces have prompted a coalition led by the United States to launch military strikes against the militants. The Houthis, a rebel group mainly consisting of Shia Muslims with ties to Iran, have controlled the capital of Sanaa and significant parts of Yemen since 2014. In 2023, they announced their intention to target ships in the Bab al Mandeb in support of Iran-backed Hamas, adding a new layer of complexity to the region’s geopolitical landscape.
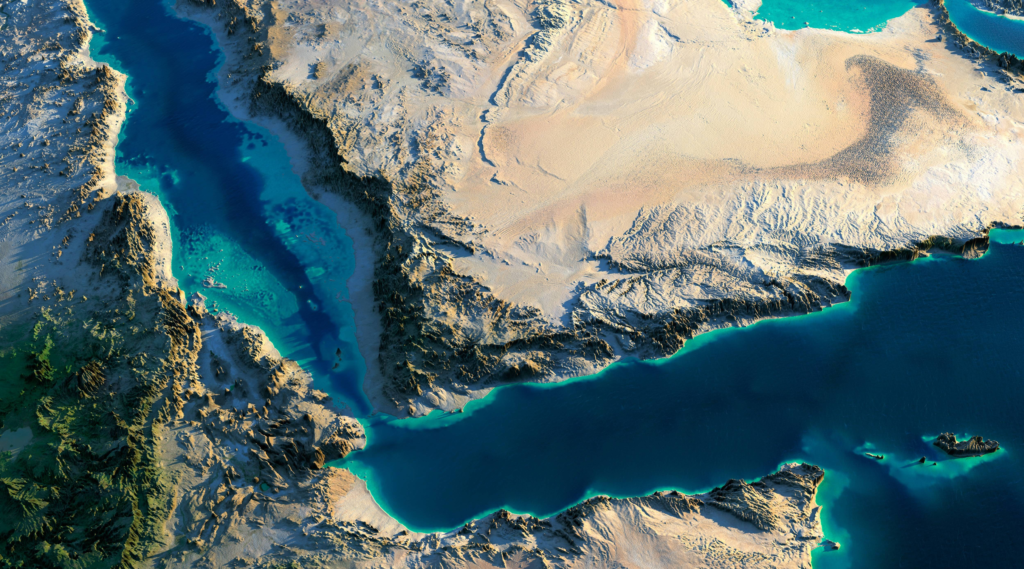

Importance in global shipping
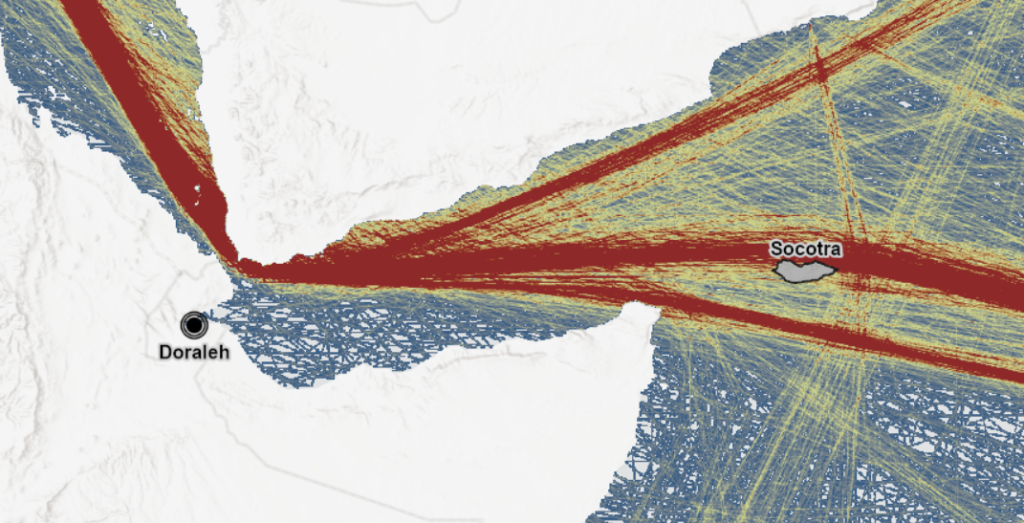
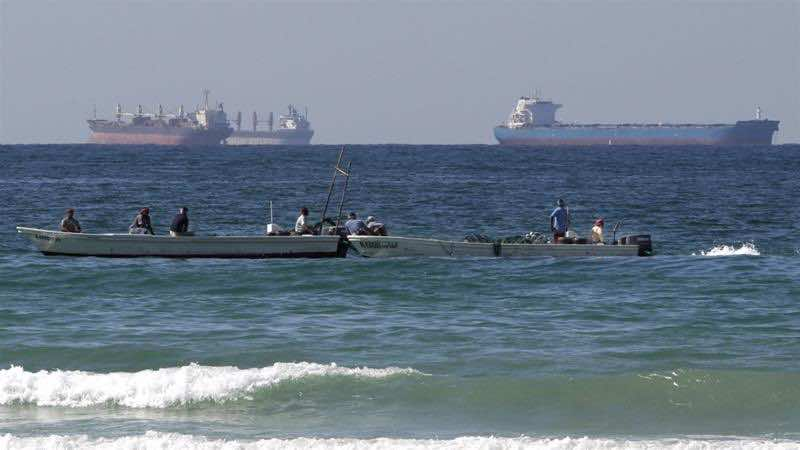
The International Maritime Organization estimates that up to a quarter of the world’s shipping, amounting to several billion tons of cargo annually, passes through the Bab al Mandeb, Red Sea, and Suez Canal. This includes around 4.5 million barrels of oil per day originating from Persian Gulf and Asian countries. The strait’s pivotal location makes it an indispensable link in the world’s key shipping route between Asia and Europe.

Historical significance
Beyond its current geopolitical importance, the Bab al Mandeb has played a significant role in human history. While it was once considered a perilous sea crossing, the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 dramatically increased shipping in the Red Sea, solidifying the Bab al Mandeb as a preferred route between Europe and Asia. The British Empire’s historical presence on the island of Perim further underlines its strategic importance in global trade.
From a prehistoric perspective, some scientists have suggested that the Bab al Mandeb may have served as a land bridge between the Horn of Africa and the Arabian Peninsula, potentially facilitating early human migration out of Africa.
Recent decades and global flashpoint
Since the 1960s, the Bab al Mandeb has evolved into a global flashpoint due to the immense volume of trade and oil passing through its waters. Major world powers, including the United States and China, have established military bases on the Djibouti side of the strait to safeguard against potential hostilities. The strait’s role in conflicts, such as the 1973 oil tanker blockade enforced by Arab nations after the Yom Kippur War, underscores its critical impact on global energy supplies.

Conclusion
As headlines continue to highlight the Bab al Mandeb’s role in contemporary conflicts, it is crucial to recognize its enduring significance in global shipping and its impact on geopolitical dynamics. The strait’s historical and present-day importance underscores the need for international cooperation and diplomacy to ensure the stability of this vital maritime corridor.
To explore more news : Click Here
ALSO READ : The World’s Deadliest Spiders : A Closer Look At 9 Dangerous Arachnids