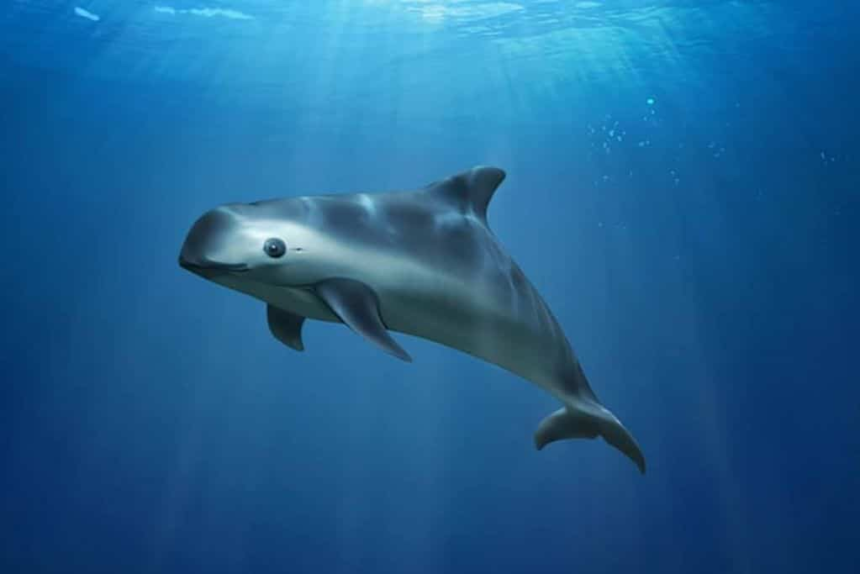
Learn about Vaquitas, the world’s most endangered marine mammal, including their habitat, population status, and behavior.
The Vaquita : Introduction
The vaquita, the smallest of the cetaceans, is teetering on the edge of extinction, holding the unfortunate title of the most endangered marine mammal in the world. With an estimated population of fewer than 30 individuals, representing a decline of over 95 percent since 1997, urgent and comprehensive conservation efforts are imperative to prevent the vanishing of this species. This article delves into the critical issues facing these mammals, focusing on the role of gillnets, the impact of totoaba fishing, and the challenges of conservation in the northern Gulf of California.
ALSO READ : Gigantopithecus : Unraveling The Enigmatic Mysteries Of The Giant Ape

The Vaquita’s habitat and unique characteristics
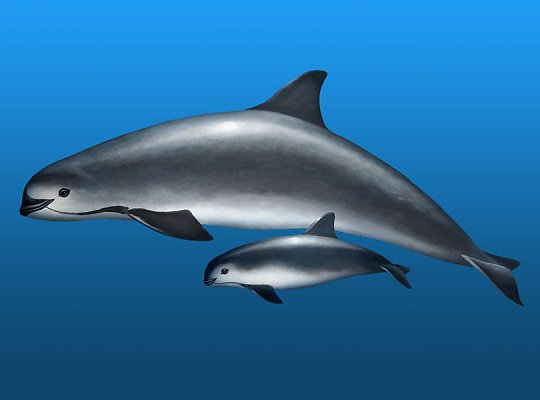
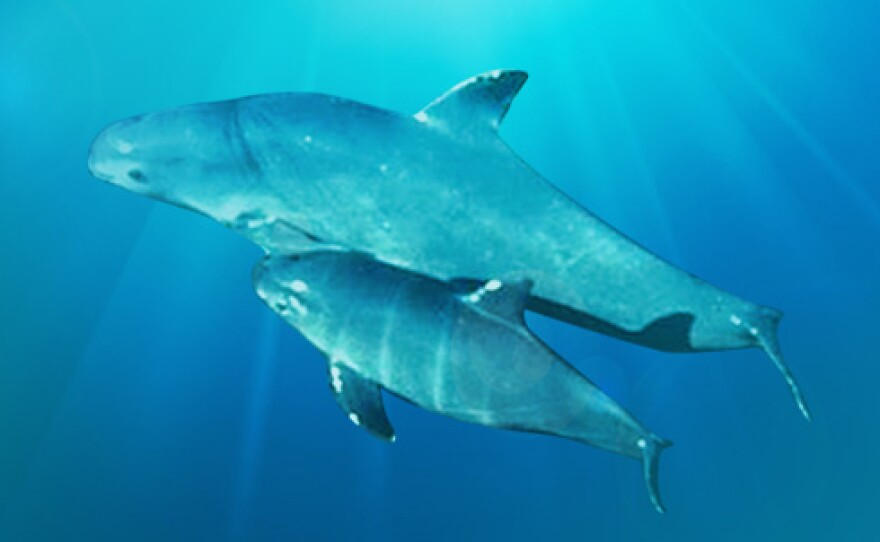
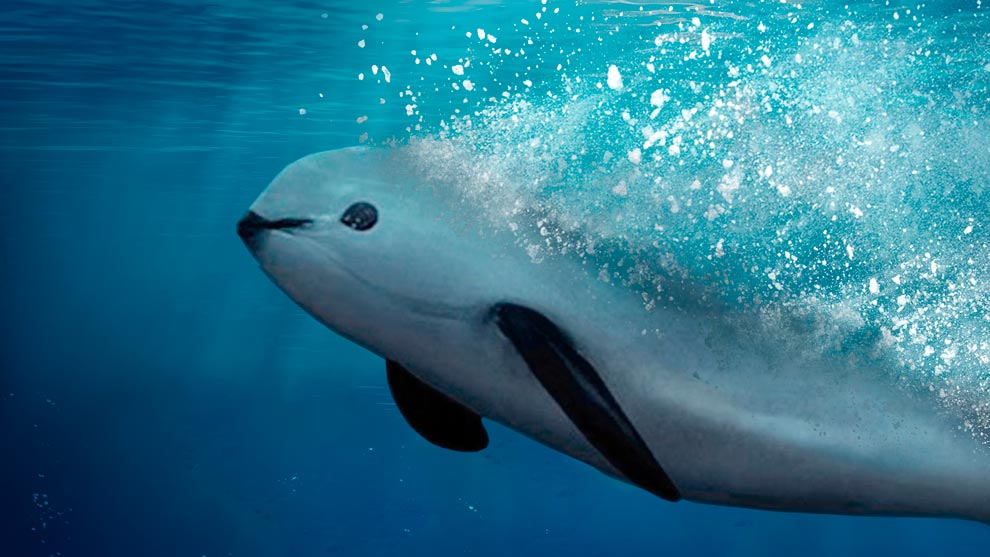
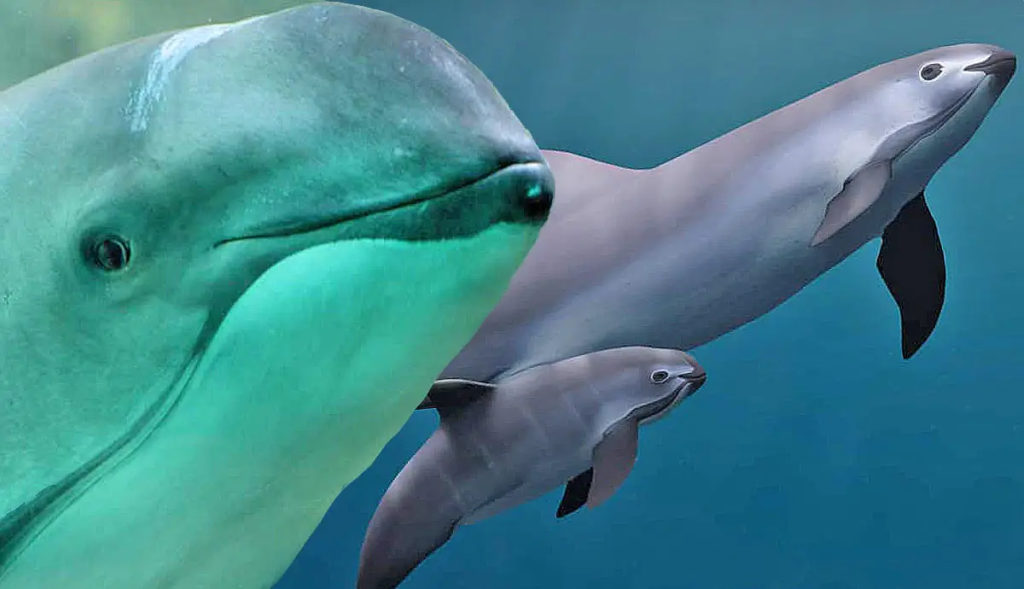
Found exclusively in the shallow waters of the northern Gulf of California, Mexico, vaquitas navigate the rich marine environment that is crucial for their survival. Measuring around 5 feet in length on average, these mammals are distinguishable by their dark gray coloration, lighter gray undersides, and distinctive black patches on their faces. Their dorsal fins, taller and wider than those of most other porpoises, add to the uniqueness of this species.
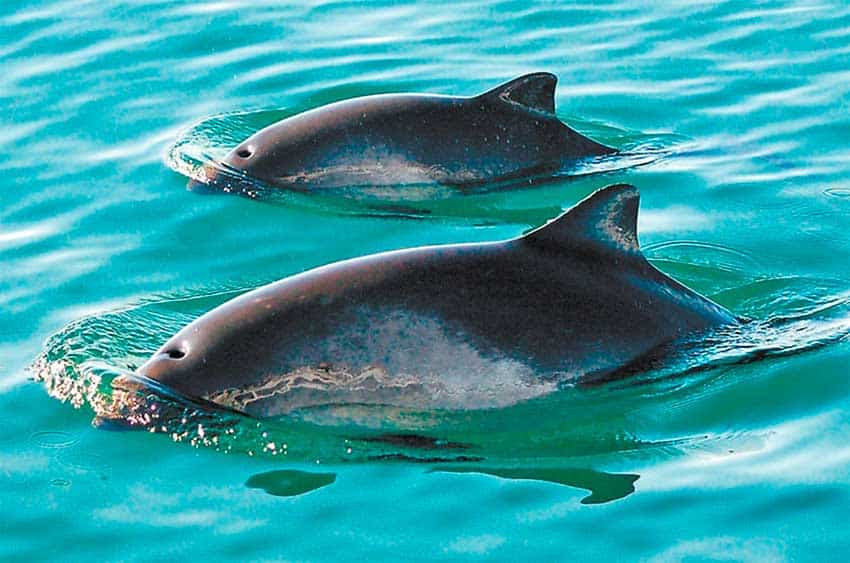

The threat of gillnets
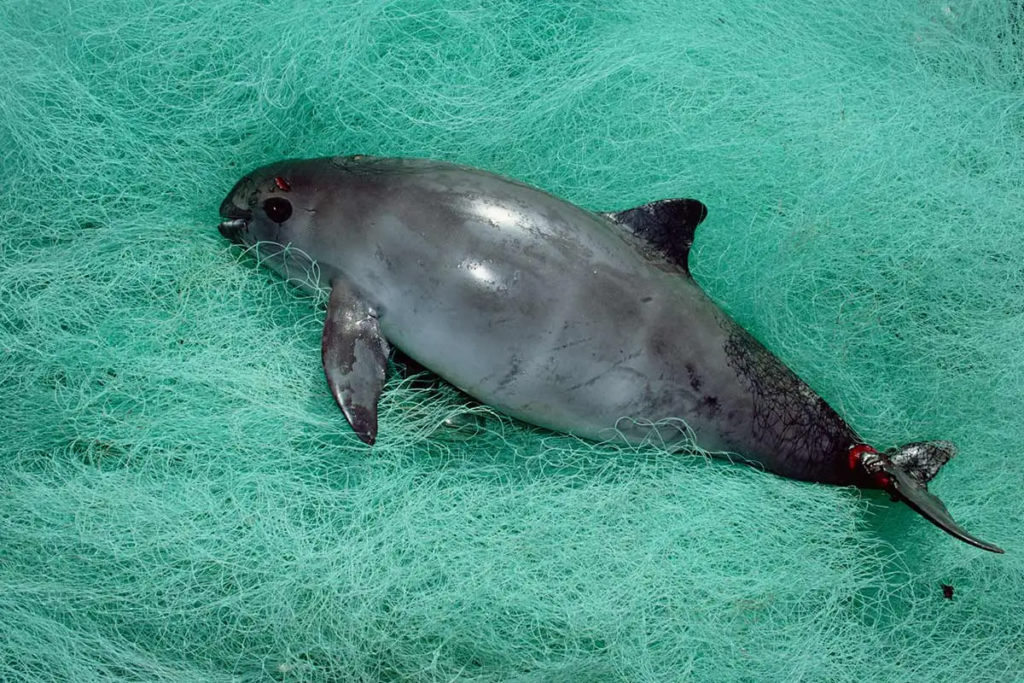
The primary threat to vaquitas is posed by gillnets, a type of fishing net extensively used in the region. Most fishers, whether legally or illegally pursuing totoaba, employ gillnets, which have proven devastating for this mammal population. Gillnets are designed to entangle fish and shrimp, but their indiscriminate nature traps vaquitas as well, leading to a drastic decline in their numbers.
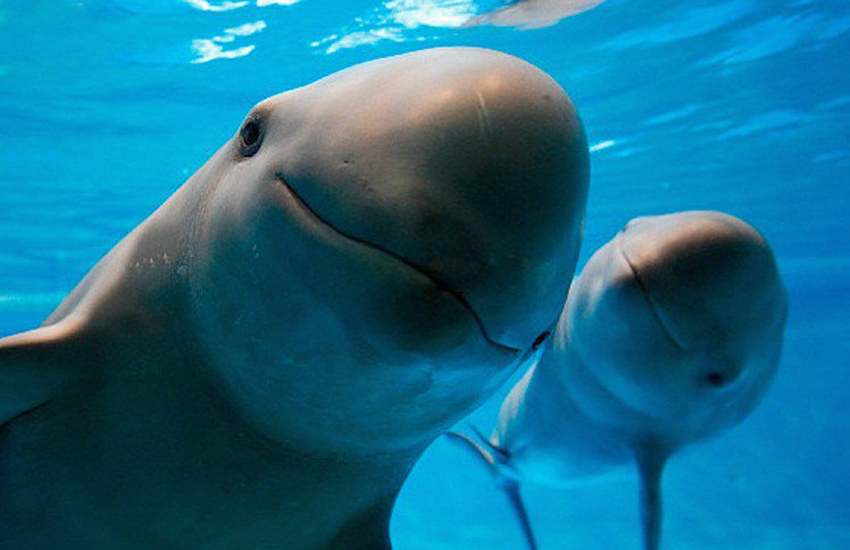

Conservation efforts
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the Mexican government has implemented several measures to safeguard the vaquita. A Vaquita Refuge in the northern Gulf of California aims to protect the species’ core range, and a compensation plan supports fishermen whose livelihoods depend on this region. Emergency bans on gillnets were enforced from 2015 to 2017, followed by a permanent ban (with limited exceptions) in mid-2017. Despite these efforts, this mammal population continues to face challenges.
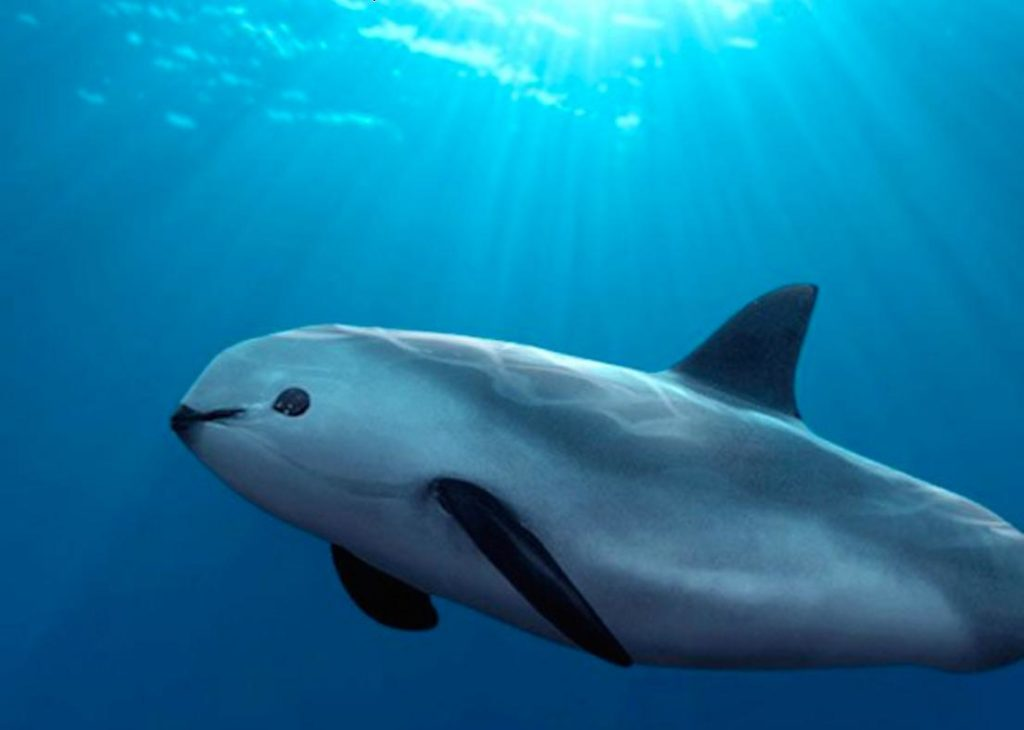

Totoaba fishing and illegal practices
The illegal fishing of totoaba exacerbates the vaquita’s decline, as both species share similar sizes, and the gillnets used for totoaba are the very nets that vaquitas are most prone to getting ensnared in. During the shrimping season, over 400 miles of gillnets are set within this mammal’s range daily, intensifying the threat to their survival.

Conservation strategies
In the face of this mammal’s alarming decline, conservationists are intensifying their efforts to protect this endangered species. Central to these initiatives is a heightened focus on enforcing existing regulations and implementing stricter measures to curb illegal fishing activities, particularly the use of gillnets. These efforts involve increased surveillance, patrols, and collaboration with local communities to ensure compliance with bans on these destructive fishing tools.
Furthermore, recognizing the need for sustainable solutions, significant attention is directed towards the development and implementation of alternative fishing gear. The goal is to provide viable and environmentally friendly alternatives to gillnets that can meet the needs of local fishermen while minimizing harm to this mammal population. This requires a collaborative approach involving marine biologists, fisheries experts, and local stakeholders to devise innovative solutions that balance ecological conservation with the livelihoods of those dependent on fishing in the Gulf of California.

During the totoaba spawning season, a critical period when illegal fishing activities intensify, special measures are enacted to mitigate the impact on vaquitas. Heightened surveillance and strategic interventions are employed to safeguard vaquitas during this vulnerable time, aiming to reduce accidental entanglements and promote the overall well-being of the remaining population.

The survival of the vaquita hinges on instigating profound changes in fishing practices within the Gulf of California. Beyond regulatory measures, it necessitates a cultural shift towards sustainable and responsible fishing practices. Collaborative educational programs are crucial to raising awareness among local communities about the importance of protecting the vaquita and the long-term benefits of adopting ecologically sound fishing methods. By fostering a sense of shared responsibility, these initiatives aim to create a sustainable coexistence between human activities and the delicate marine ecosystems upon which the vaquita depends.

Challenges and future prospects
The challenges in conserving vaquitas are multi-faceted, requiring not only effective enforcement but also collaboration with local communities dependent on fishing. Developing sustainable alternatives to gillnets and addressing the root causes of illegal totoaba fishing are crucial steps in ensuring the vaquita’s survival.

Conclusion
The vaquita’s precarious existence serves as a stark reminder of the urgent need for concerted global efforts to protect endangered species and preserve marine biodiversity. With a population on the brink of extinction, the fate of the vaquita hangs in the balance, necessitating swift and effective conservation actions to secure a future for this unique marine mammal in the northern Gulf of California.
To explore more news : Click Here
ALSO READ : The American Bison Dilemma : Conservation Challenges On Catalina Island




































