Learn about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hearing loss after ear infection that may occur after an ear infection, including the importance of seeking medical attention for proper diagnosis and management.
Hearing loss after ear Infection can occur for various reasons, and one common cause is an ear infection. While ear infections are typically associated with pain and discomfort, they can also lead to temporary or permanent hearing loss in some cases. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hearing loss that may occur after an ear infection.
Understanding Hearing Loss After Ear Infection
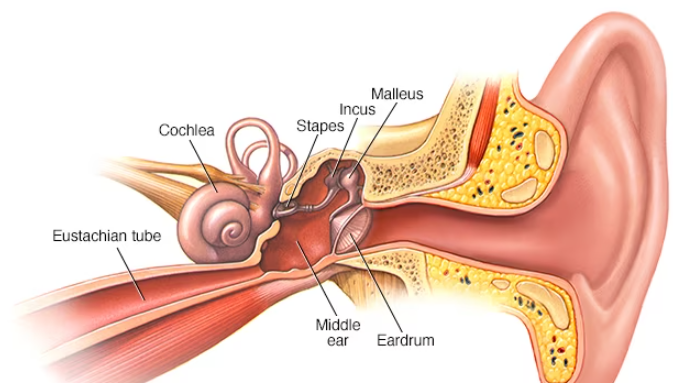
Ear infections, also known as otitis media, can affect the middle ear, causing inflammation and fluid buildup behind the eardrum. When left untreated or inadequately treated, ear infections can lead to complications, including hearing loss. The presence of fluid in the middle ear can interfere with the transmission of sound waves, resulting in temporary or permanent hearing impairment.
Also read-Unveiling The Symbolism: The Mental Illness Flag And Its Significance In Mental
Hearing Loss After Ear Infection
Causes of Hearing Loss After Ear Infection
Several factors can contribute to hearing loss following an ear infection:
- Fluid Accumulation: The buildup of fluid in the middle ear during an ear infection can impair the movement of the eardrum and the tiny bones in the middle ear responsible for transmitting sound vibrations.
- Damage to Ear Structures: Severe or chronic ear infections can cause damage to the delicate structures of the middle ear, including the eardrum and the ossicles (tiny bones). This damage can interfere with the transmission of sound and lead to hearing loss.
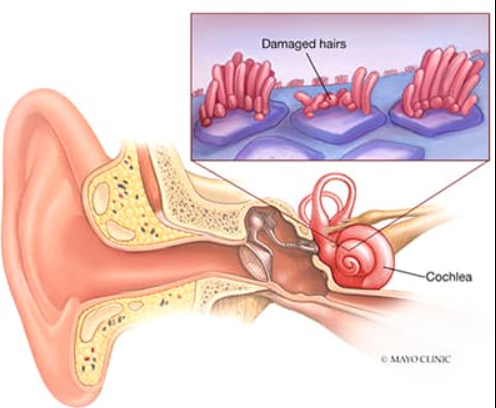
- Inner Ear Damage: In some cases, the infection or inflammation may spread to the inner ear, where the cochlea (the organ of hearing) is located. Damage to the cochlea can result in sensorineural hearing loss, which is often permanent.

Symptoms of Hearing Loss After Ear Infection
The symptoms of hearing loss after an ear infection may vary depending on the severity and duration of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Difficulty hearing or understanding speech, especially in noisy environments
- Muffled or distorted sound perception
- Ringing or buzzing sensation in the ears (tinnitus)
- Ear pain or discomfort
- Drainage of fluid or pus from the ear (in cases of severe infection)
It’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as prompt diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further complications and improve outcomes.

Treatment Options for Hearing Loss After Ear Infection
The treatment approach for hearing loss after an ear infection may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Treatment options may include:
- Antibiotics: If the hearing loss is due to an active ear infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to clear the infection and reduce inflammation in the middle ear.
- Ear Tube Placement: In cases of recurrent or chronic ear infections with persistent fluid buildup, a surgical procedure known as tympanostomy or ear tube placement may be recommended. Ear tubes help ventilate the middle ear and prevent fluid accumulation, reducing the risk of hearing loss.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroid medications may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling in the middle ear, especially in cases of sensorineural hearing loss associated with inner ear damage.
- Hearing Aids: For individuals with permanent hearing loss, hearing aids may be recommended to amplify sound and improve communication. Hearing aids come in various styles and configurations to suit individual needs and preferences.
- Cochlear Implants: In severe cases of sensorineural hearing loss where hearing aids are not effective, cochlear implants may be considered. Cochlear implants are electronic devices surgically implanted in the inner ear to bypass damaged hair cells and directly stimulate the auditory nerve.
Conclusion of Hearing Loss After Ear Infection
Hearing loss following an ear infection can have significant implications for communication, social interaction, and overall quality of life. It’s essential to recognize the symptoms of hearing loss and seek prompt medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the causes and treatment options for hearing loss after an ear infection, individuals can take proactive steps to preserve their hearing health and address any hearing-related concerns effectively. If you or a loved one experience hearing loss symptoms after an ear infection, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized evaluation and management.

Also read-Diet 101 For The Autoimmune Protocol (AIP): Advice, Methods Of preparation, And Planning Lists
images source: Google
Disclaimer: The opinions and suggestions expressed in this article are solely those of the individual analysts. These are not the opinions of HNN. For more, please consult with your doctor