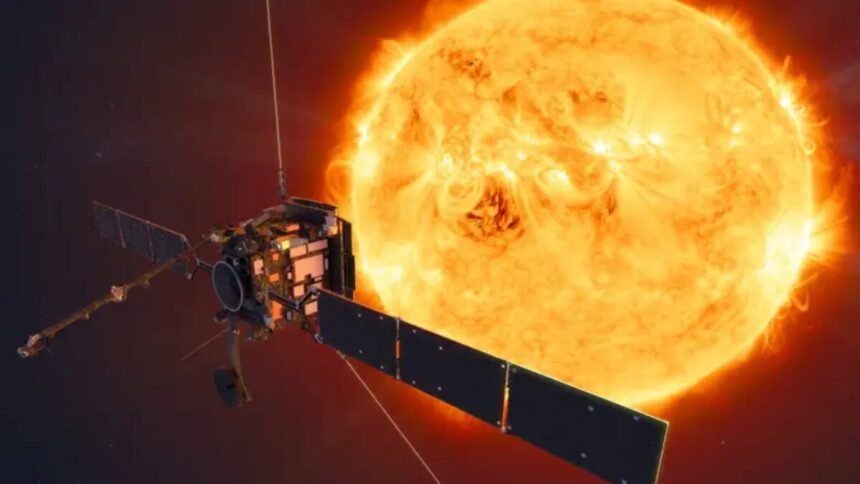
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has always been at the forefront of space exploration, showcasing remarkable advancements in technology and a deep commitment to scientific discovery. One of its most ambitious upcoming missions is the Aditya L1 Mission, which aims to unlock the mysteries of the Sun and expand our understanding of the solar system’s central star.
Introduction to The Mission
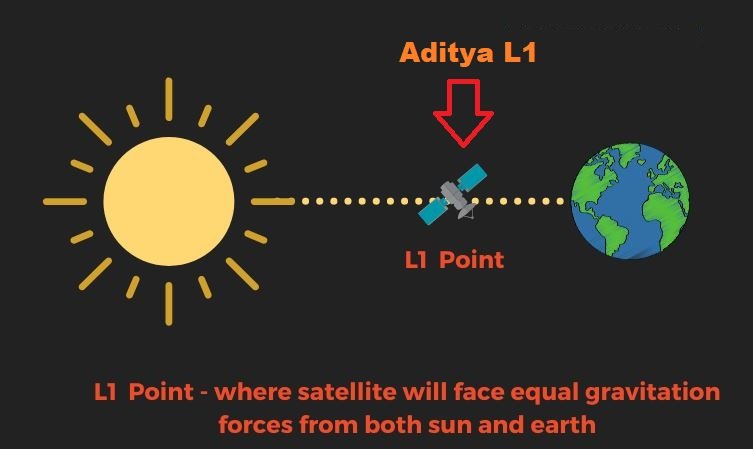
Named after the Hindu Sun god “Aditya,” the Aditya L1 Mission is designed to study the Sun’s outermost layer, the corona, and its magnetic field. This mission represents a significant step in our quest to comprehend the fundamental processes that govern the Sun’s behavior, as well as its impact on the Earth and space weather.
Scientific Objectives
The primary scientific objectives of the Aditya L1 Mission are multifaceted and impactful:
- Understanding Solar Corona: The corona, the Sun’s outer atmosphere, is a region of extreme temperatures and dynamic magnetic fields. However, its behavior and mechanisms remain largely enigmatic. Aditya L1 aims to observe the corona with unprecedented detail, shedding light on its heating mechanisms, temperature variations, and origin of solar winds.
- Studying Solar Wind: The solar wind, a continuous stream of charged particles emitted by the Sun, plays a crucial role in shaping space weather. This phenomenon can influence satellite operations, communication systems, and even power grids on Earth. Aditya L1’s observations will provide valuable insights into the solar wind’s dynamics and its interaction with the Earth’s magnetosphere.
- Exploring Magnetic Fields: The Sun’s magnetic fields are responsible for its various activities, including sunspots, flares, and prominences. By studying these magnetic fields in detail, the mission aims to understand their evolution and how they contribute to the Sun’s overall behavior.
Technical Aspects
The Aditya L1 spacecraft will be equipped with a suite of advanced instruments to carry out its scientific investigations. One of the standout instruments is the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), which will capture images of the corona by blocking the Sun’s disk. Another critical instrument is the Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT), which will provide insights into the chromosphere and transition region of the Sun’s atmosphere.
Impact and Significance
The knowledge gained from the Aditya L1 Mission is expected to have far-reaching implications. It will enhance our ability to predict and mitigate the effects of space weather events on Earth, safeguarding crucial technological systems. Additionally, the mission’s findings could contribute to advancements in fusion research and renewable energy technologies, given that the Sun is a massive fusion reactor.
Conclusion
The Aditya L1 Mission stands as a testament to India’s growing prowess in space exploration and scientific inquiry. By delving into the mysteries of the Sun, ISRO is not only expanding our understanding of our local cosmic environment but also contributing to the global scientific community’s quest for knowledge. As the mission unfolds and the data starts flowing in, the world eagerly anticipates the insights that Aditya L1 will provide, taking us one step closer to unraveling the secrets of our Sun.




































