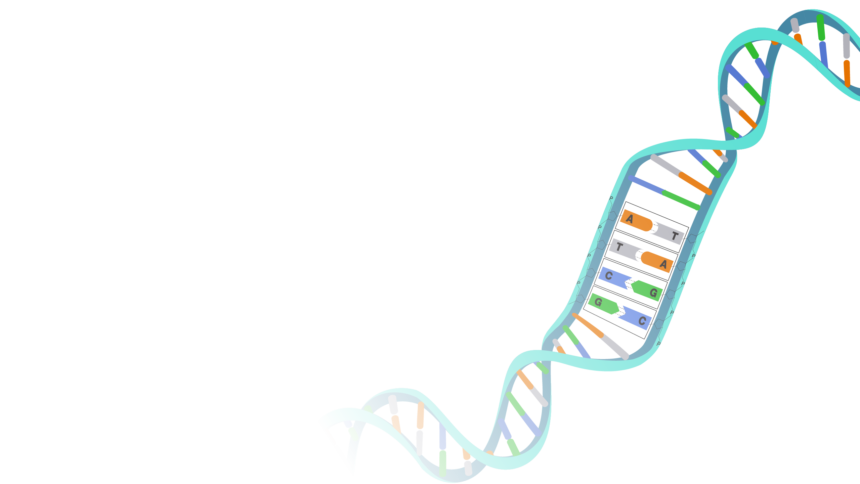
Deoxyribonucleic Acid better known as DNA, is a remarkable molecule that encodes the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known living organisms. It is the foundation of genetics, offering a fascinating glimpse into the origins of our traits and characteristics. This article delves into the world of DNA, explaining where your genes come from and how this incredible molecule shapes your identity.
What is DNA?
Just consider it. Four DNA letters—A, T, G, and C—combine to determine your unique identity.
Your body contains so much DNA that it could stretch to the moon.
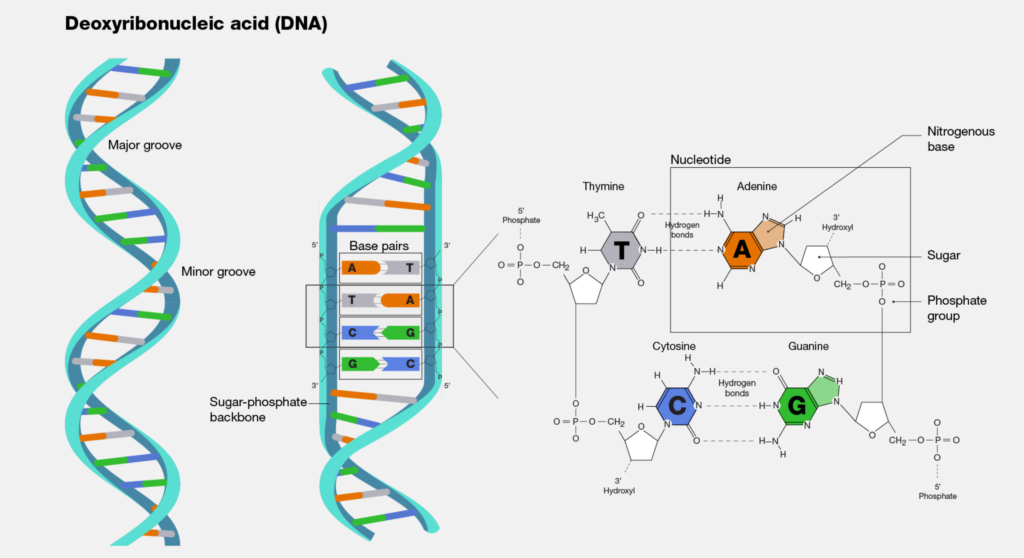
DNA builds protein molecules in order to function. In the end, your identity is mostly determined by protein molecules. It bestows upon you, for instance, certain physical and psychological qualities.
“All living things have DNA. Like an instruction manual, DNA instructs your body how to build itself and behave.”
ALSO READ : The Secret Code Of Nature: The Way Plants “Speak” Through The Air Via VOC
The RNA chicken and the DNA egg
A brief summary of the distinctions between DNA and RNA. Genetic information is carried by both DNA and RNA.
DNA: DNA cannot leave the nucleus.
RNA: RNA has the ability to exit the nucleus and replicate the data present in DNA. It locates a ribosome after exiting the nucleus so that it can begin synthesising proteins. In the end, your identity is determined by the molecules of proteins.
So which came first, like the chicken and the egg? Scientists are at a loss for a solution. Because RNA has a simpler structure than DNA, most biologists think it existed before DNA. RNA has the ability to cling to other molecules and accelerate chemical reactions.
For this reason, researchers thought that the first DNA was produced by RNA. RNA developed into a world dominated by DNA because DNA is a greater information storage than RNA.
RNA and DNA are the building blocks of life
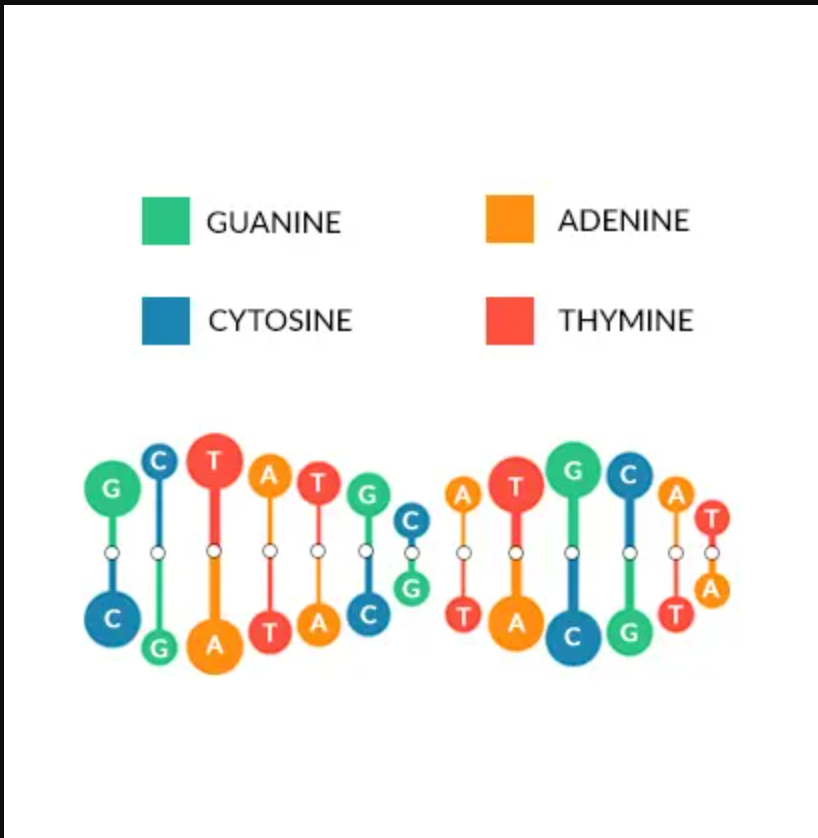
The origins of DNA are unknown to us. It is impossible for scientists to recreate the spark that created the chemical building elements of life. It was formerly thought by scientists that the extreme heat of the late heavy bombardment period sterilised the surface of Earth. Put another way, at that time, bacteria could not withstand the extreme circumstances on Earth.
However, the events that occurred during this turbulent period of Earth’s history might have produced undersea and underground habitats. Any microbiological life on Earth could find sanctuary as its own home within these hydrothermal vents.
In an attempt to reproduce the beginnings of life, scientists are attempting to replicate the circumstances and collisions that occurred. Here, the conditions were ideal for the synthesis of organic molecules and amino acids from inorganic materials.
There is compelling evidence that all living organisms descended from the last universal common ancestor (LUCA), who lived approximately 4 billion years ago. Eukaryotes eventually developed through endosymbiosis. During the Cambrian explosion, varied life finally began to develop.
DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid
DNA, also known as deoxyribonucleic acid, is a type of nucleic acid that contains the genetic information necessary for the growth and operation of all known living things as well as several viruses.
It has the genetic instructions needed to make proteins, which are subsequently utilised to make cells and living things.
Please feel free to ask any questions you may have regarding deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in the comments section below.
DNA and Genetic Diversity
It’s important to note that our DNA is remarkably diverse, and small variations in DNA sequences can lead to significant differences in traits. This diversity is why siblings can have distinct characteristics, even though they share the same parents.
Genetic Research and the Human Genome

The study of DNA and genetics has seen rapid advancements in recent decades, leading to the mapping of the human genome. The Human Genome Project, initiated in the early 1990s, was an international research effort that aimed to identify and map all the genes of the human species. This monumental undertaking was completed in 2003, resulting in a detailed map of the entire human genetic code. It has paved the way for profound insights into human genetics, offering a deeper understanding of where our genes come from and their role in health, development, and heredity.
Conclusion
DNA is the fundamental molecule that determines where your genes come from and shapes your genetic identity. It is a remarkable molecule with a double helix structure that contains the genetic code for building and maintaining living organisms. Genetic inheritance, guided by Mendelian principles, underlies the diversity of traits and characteristics observed in the human population. As our understanding of genetics advances, the secrets encoded in DNA continue to reveal the origins of our genes and the intricacies of our genetic heritage.
ALSO READ : Natural Selection Surprises: Evolutionary Insights From Florida’s Wild Lizards




































