Introduction
Pangea Ultima, a concept that once belonged to the realm of geological speculation, is increasingly becoming a topic of serious discussion among scientists and geologists. The idea of Earth’s continents reassembling into a supercontinent is not new, but the potential implications of Pangea Ultima for Earth’s ecosystems, especially mammalian life, are a source of growing concern. In this article, we delve into the intriguing concept of Pangea Ultima and its potential impact on mammalian biodiversity.
Pangea Ultima: A Supercontinental Reunion
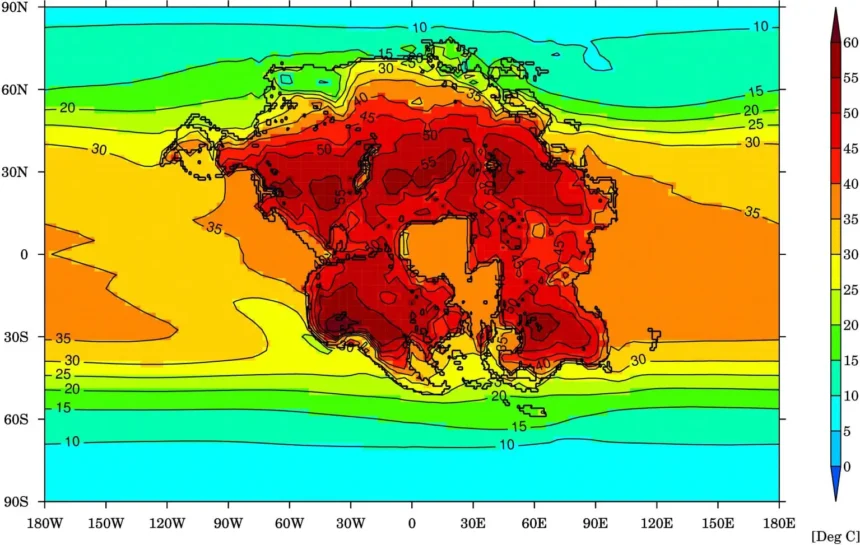
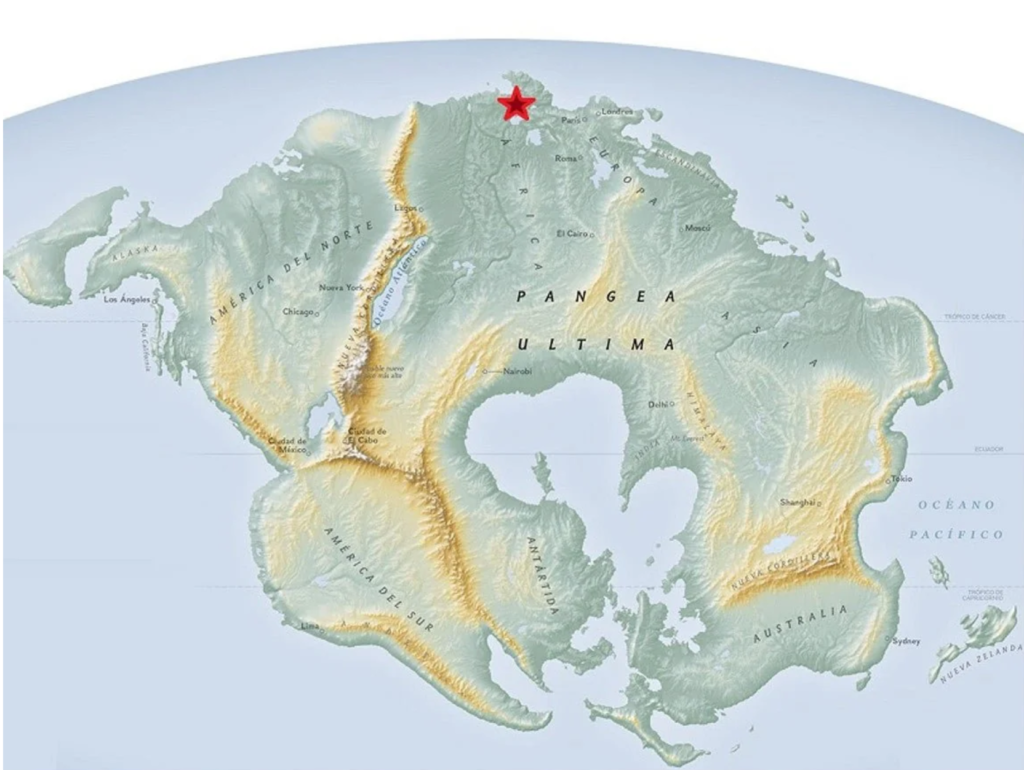
Pangea Ultima is a theoretical supercontinent that is predicted to form in the distant future. It is a continuation of the cycle of supercontinent formation and breakup that has occurred throughout Earth’s history. The name “Pangea Ultima” translates to “Last Pangea,” signifying the belief that this will be the final supercontinent before the cycle begins anew.
Geological models suggest that this supercontinent could start forming within the next 200 to 300 million years. As Earth’s tectonic plates continue their slow movements, they will converge, eventually leading to the amalgamation of all continents into a single landmass.
Mammalian Biodiversity at Risk
While the formation of Pangea Ultima might seem like a distant event with minimal impact on current life, the potential consequences for mammals are significant. Mammals, including humans, are highly adapted to the current distribution of continents. The continents act as barriers that shape biodiversity and allow species to evolve separately. With the formation of a supercontinent, these barriers disappear, leading to several challenges for mammals:
- Loss of Biodiversity: The amalgamation of continents would lead to the mixing of species that have evolved separately for millions of years. This can result in competition for resources, leading to the extinction of some species and a dramatic reduction in biodiversity.
- Habitat Disruption: Mammals are closely tied to their specific habitats. The radical changes in geography could disrupt ecosystems and force species to adapt rapidly or face extinction.
- Invasive Species: As continents merge, species from one continent could invade ecosystems on another. These invasive species can outcompete and prey on native species, further destabilizing ecosystems.
- Climate Change: The rearrangement of landmasses can also have a profound impact on climate patterns. Changes in ocean currents, wind patterns, and temperature gradients could alter habitats and potentially lead to further extinctions.
- Adaptation Challenges: Mammals will face the challenge of adapting to the new environments created by Pangea Ultima. Some species may thrive in the new supercontinent, while others may struggle to adapt to the altered conditions.
ALSO READ ; From Volcanoes To Rainforests, Here Are The 5 Largest U.S Islands
The Role of Conservation
The potential threats posed by Pangea Ultima to mammalian biodiversity underscore the importance of conservation efforts today. Protecting natural habitats, preventing the introduction of invasive species, and mitigating the impact of climate change are essential for ensuring the survival of mammalian species in the face of changing environments.
Scientists and policymakers should consider the long-term implications of geological events like Pangea Ultima and work toward strategies to mitigate potential threats to biodiversity. Additionally, research on the adaptability and resilience of mammalian species can help inform conservation efforts in the future.
Preparing for Pangea Ultima
source: reddit
Understanding and preparing for the potential challenges posed by Pangea Ultima requires an interdisciplinary approach. Scientists, conservationists, and policymakers must collaborate to develop strategies that promote species’ adaptability and resilience. Here are some considerations for preparing for Pangea Ultima:
- Habitat Corridors: Creating habitat corridors that connect different regions can help species migrate and adapt to the changing landscape. These corridors should be designed to facilitate the natural movement of wildlife.
- Biodiversity Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of biodiversity is crucial. Understanding how species are responding to changing environments can inform conservation efforts and help identify species that may be particularly vulnerable.
- Conservation Prioritization: Identifying species that are most at risk and prioritizing their conservation efforts is essential. Conservation organizations should allocate resources to protect and restore the habitats of these vulnerable species.
- Genetic Diversity: Maintaining genetic diversity within species is vital for their long-term survival. Conservation breeding programs and the preservation of genetic diversity in gene banks can aid in this effort.
- Climate-Resilient Ecosystems: Investing in climate-resilient ecosystems can help protect against the impacts of climate change associated with supercontinent formation.
- International Cooperation: Pangea Ultima, like climate change, is a global issue. International cooperation and agreements are necessary to address the challenges presented by the formation of a supercontinent.
- Public Awareness: Raising public awareness about the potential impacts of Pangea Ultima on mammalian biodiversity is essential. Public support for conservation efforts and responsible land use can make a significant difference.
Adaptation and Resilience
The adaptability and resilience of mammalian species will play a pivotal role in their survival during and after the formation of Pangea Ultima. Evolutionary processes will be put to the test, and some species may adapt successfully to the new environmental conditions. However, others may struggle, leading to population declines or extinctions.
Research into the mechanisms of adaptation, including genetic and behavioral changes, will be crucial. Conservationists can use this knowledge to implement interventions that assist struggling species. Such interventions might include habitat restoration, translocation efforts, or the creation of protected environments that mimic the species’ original habitats.
Conclusion
Pangea Ultima, the theoretical formation of a supercontinent in the distant future, raises complex questions about the potential consequences for mammalian biodiversity. While this geological event is far from imminent, it serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems and the importance of long-term planning and conservation efforts.
Preparing for Pangea Ultima is a multidisciplinary challenge that requires a combination of habitat preservation, conservation initiatives, and international cooperation. It also necessitates a deep understanding of how species can adapt to rapidly changing environments. The fate of Earth’s mammals in the face of such geological transformations will depend on our ability to comprehend, prepare for, and mitigate potential threats to biodiversity.
ALSO READ :Natural Selection Surprises: Evolutionary Insights From Florida’s Wild Lizards