Dive into Thailand’s currency system, history, and denominations. Get a clear picture of Thai Baht and its importance.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the intricacies of Thailand currency, shedding light on everything you need to know about the Baht and its role in the vibrant Thai economy.As your trusted source of information, we aim to equip you with a thorough understanding of Thailand’s currency landscape, helping you navigate this beautiful Southeast Asian nation with confidence.
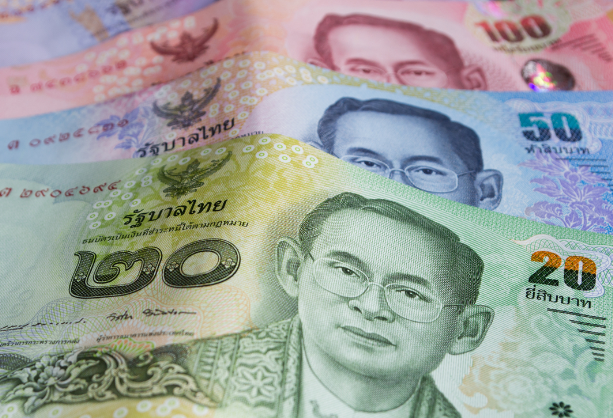

The Thai Baht: An Introduction
The Foundation of Thai Finance
The Thai Baht, denoted by the sign and abbreviated as ฿, is the country of Thailand’s official currency. The Baht is the backbone of the country’s finances, being essential to trade, investment, and day-to-day dealings. Any traveler, whether on vacation or on business, who wants to experience Thailand must be familiar with this currency.

A Brief Historical Overview Of Thailand Currency
Tracing the Baht’s Origins
We must go back in time to fully understand the Thai Baht. The Baht was first used in the 19th century under the rule of King Chulalongkorn, also known as Rama V, and has a long history. The currency was initially based on the silver standard, although it has since undergone major change.

Modern Thai Baht
The Baht’s Evolution
The Thai Baht is a fiat currency today, which means that it isn’t backed by any real assets like gold or silver. It gets its worth instead from the robustness and stability of the Thai economy. The Baht is issued and governed by the Bank of Thailand, the country’s central bank, to maintain its stability.
Currency Denominations
Breaking It Down
The Thai Baht is broken into smaller pieces, with coins and banknotes having the highest circulation. Banknotes come in denominations of 20, 50, 100, 500, and 1,000 Baht, while coins are available in 1, 2, 5, and 10 Baht. These many denominations make it easier to conduct daily business and guarantee that you can always find a type of currency that meets your requirements.

Exchange Rates
Navigating Currency Conversion
It’s essential to comprehend exchange rates while working with international money. When exchanging money, it’s important to be aware of the most recent exchange rates because the value of the Thai Baht can change. You may check this by using reputable currency conversion websites and applications, local banks, and exchange bureaus.
Currency Symbols
Deciphering Currency Codes
There are many different codes and symbols that you could encounter when working with Thai cash. The worldwide currency code for the Thai Baht is ฿, in addition to the official symbol of. Understanding these symbols can be useful when making financial transactions or looking up information about currencies.

The Role of the Baht in Thailand’s Economy
A Driving Force
The Thai Baht is essential to the economy of the country. It is generally accepted in both urban and rural regions and acts as the principal means of trade for goods and services. A significant indicator for investors and economists, the currency also indicates Thailand’s overall economic health.
Where to Exchange Currency
Where to Exchange Money
Thailand offers various options for exchanging your currency into Thai Baht. The most common places include:
- Banks: Banks in Thailand provide reliable exchange services, and you’ll often find competitive rates. It’s best to exchange your currency at major banks or authorized exchange counters.
- Currency Exchange Kiosks: These are prevalent at airports, shopping centers, and tourist hubs. While convenient, be cautious of hidden fees and less favorable rates at some kiosks.
- ATMs: ATMs are widely available in Thailand and accept international credit and debit cards. This can be a convenient way to withdraw Baht, but keep in mind the foreign transaction fees imposed by your bank.

Tips for Handling Thai Baht
Maximizing Convenience
- To make the most of your trip to Thailand, here are some tips for handling Thai Baht efficiently:
- Despite the fact that cards and cash are both commonly accepted, having a credit or debit card can be useful, particularly for larger purchases.
- ATM fees should be considered: When using ATMs in Thailand, be aware of any potential additional fees. The ATM operator in your area and your bank could impose withdrawal fees.
- Maintain lower denominations: Having coins and smaller currencies on hand is helpful for daily expenses and tips.
- Visit reputable sources to exchange currency: To guarantee that you receive correct rates and genuine currency, choose reputable banks or authorized exchange counters.

Conclusion
Mastering Thailand’s Currency
In conclusion, a seamless and joyful trip in this fascinating country depends on your ability to use the local currency, the Thai Baht. The Baht is at the center of Thailand’s financial environment, from its historical roots to its contemporary significance in the economy. With this information in hand, you can tour the Land of Smiles with assurance, knowing that you have a firm understanding of its monetary system.
Also Read: Maldives Currency: A Comprehensive Guide
image source: google




































