Introduction
The question of what is sacrosanct whether it’s the Indian Constitution or the holy books of religion, is a complex and sensitive one. It touches upon matters of law, governance, and faith. In the diverse and pluralistic democracy of India, both the Constitution and religious texts hold profound significance, albeit in different ways. This article aims to explore the roles and the unique positions of the Indian Constitution and religious texts in the context of Indian society.
The Indian Constitution: The Supreme Law
The Indian Constitution is the supreme law of the land and the foundational document that governs the world’s largest democracy. It was adopted on January 26, 1950, and is a remarkable and comprehensive legal framework that sets out the structure of the Indian state, its principles, and the fundamental rights and duties of its citizens.
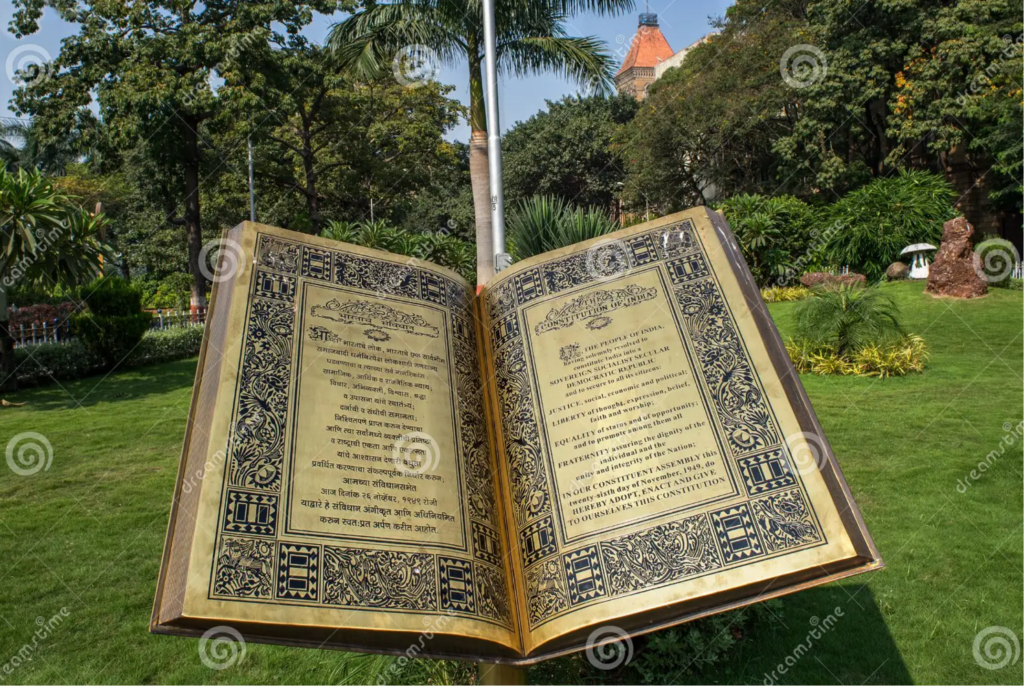

- Rule of Law: The Constitution establishes the principle of the rule of law, ensuring that no individual, institution, or government is above the law. It serves as the ultimate legal authority in the country, guiding governance and legal proceedings.
- Secularism: The Indian Constitution is founded on secular principles, emphasizing religious freedom and the separation of religion from the state. This secures the right of every individual to practice their religion without discrimination.
- Equality and Inclusivity: It enshrines principles of equality, justice, and social inclusivity. The Constitution is the embodiment of India’s commitment to protect and promote the rights and well-being of its diverse population.
- Amendment Process: While the Constitution can be amended, the process is rigorous and intended to safeguard its core values and principles.
- Protection of Rights: The Constitution provides a framework for safeguarding fundamental rights, including freedom of speech, the right to equality, and the right to religious freedom.
ALSO READ : Vienna Convention 1961: A Comprehensive Insight
Religious Texts: Matters of Faith and Morality
Religious texts, on the other hand, hold deep religious and moral significance in the lives of millions of people across India. They are revered scriptures that guide the beliefs, practices, and moral codes of different religious communities. These texts vary widely across different faiths, including Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, and others.

- Spiritual Guidance: Religious texts provide spiritual guidance and teachings that form the core of religious faith and practices. They serve as the moral and ethical compass for adherents of a particular faith.
- Cultural and Social Influence: Religious texts are not just about spiritual matters; they also have profound cultural, social, and historical influence. They shape rituals, customs, and traditions that are an integral part of people’s lives.
- Freedom of Religion: India’s secular principles and the Constitution protect the freedom of individuals to follow their religious beliefs, including the reading and propagation of their respective religious texts.
Harmony and Coexistence
India’s constitutional framework is designed to accommodate religious diversity, ensuring harmony and coexistence among various religious communities. The framers of the Constitution recognized the importance of religious pluralism and the need to protect the religious rights of all citizens.
- Principle of Secularism: The Indian Constitution, through its secular principles, seeks to maintain an equitable balance between religious and secular matters.
- Equality Before Law: The Constitution mandates that all citizens, regardless of their religious beliefs, are equal before the law and enjoy equal protection of their rights.
Balancing the Scales: A Delicate Task
Balancing the significance of the Indian Constitution and religious texts in India is not a straightforward task. It requires delicacy, respect for diverse beliefs, and a commitment to upholding the values enshrined in the Constitution. Here are a few key considerations:

- Secularism: India’s secularism is a constitutional principle that is fundamental to its identity. It ensures that the government remains neutral in matters of religion and guarantees the right to religious freedom. The Constitution provides a clear framework for resolving disputes and conflicts related to religion.
- Religious Pluralism: India’s religious diversity is one of its most defining features. Upholding this diversity while safeguarding individual and collective religious rights is a core aspect of the nation’s identity. The Constitution ensures that all religious communities are treated equitably.
- Rule of Law: The Constitution, as the supreme law of the land, establishes the rule of law. It is essential that the law be followed and respected by all individuals and communities, regardless of their religious beliefs. This legal framework is the bedrock of a democratic and just society.
- Dialogue and Understanding: Encouraging dialogue and understanding between communities is crucial. It fosters mutual respect and a spirit of coexistence. It’s important to recognize that diverse religious communities can learn from each other, contributing to the nation’s cultural richness.
- Education and Awareness: Promoting education and awareness about the Constitution, religious texts, and the principles of religious pluralism is a key way to ensure that citizens understand their rights and responsibilities.
The Way Forward: Harmony and Respect
The coexistence of the Indian Constitution and religious texts exemplifies the harmony and respect that India aspires to uphold. The Constitution provides a framework for governance, justice, and equality, ensuring that the rights of every citizen are protected. Religious texts, in their diverse forms, guide the spiritual and moral lives of countless Indians.
As the nation continues to evolve, it is essential to remember that the Constitution and religious texts are not in opposition. Instead, they complement each other, serving distinct but interconnected roles in the lives of individuals and the functioning of a pluralistic society. Their coexistence is a testament to India’s commitment to diversity, unity, and the shared values that form the tapestry of the nation’s identity. In upholding these principles, India can continue to be a shining example of harmonious coexistence in a complex and interconnected world.
ALSO READ :The Diminishing Influence of the United Nations: A Global Perspective