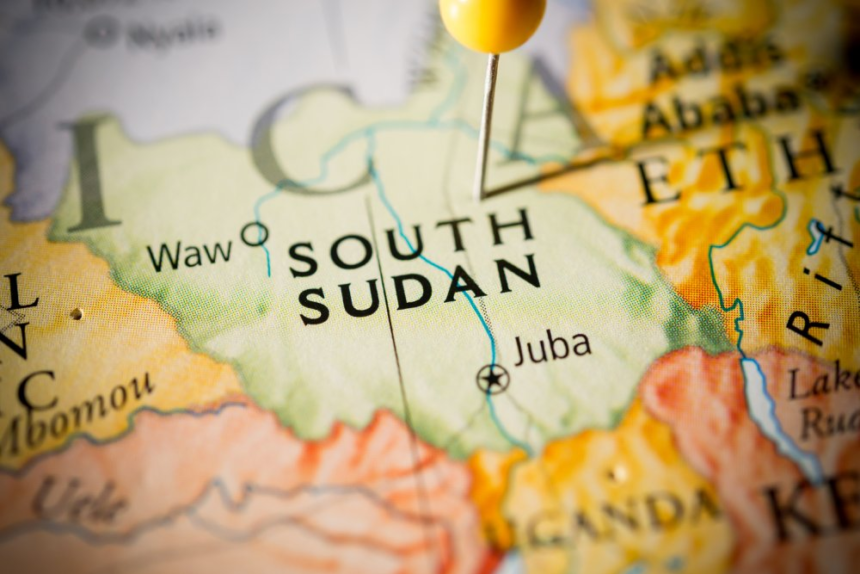
Explore the historical journey that led to South Sudan becoming the newest country in the world. Delve into the events and decisions that shaped its independence.
The newest country in the world : Introduction
The newest country in the world : New countries don’t emerge every day, and the process of gaining international recognition as an independent state is complex. The newest internationally recognized country in the world is South Sudan, an African nation that declared independence on July 9, 2011. This article explores the factors that contribute to the creation of new countries, the international legal criteria, and the specific historical context that led to South Sudan’s establishment as an independent nation.
ALSO READ : Africa’s Vultures In Peril : A Grim Outlook For The Continent’s Raptors

The Montevideo convention and criteria for statehood
The newest country in the world : The establishment of new countries is a complex process, governed by widely acknowledged criteria deeply entrenched in international law. One of the pivotal milestones in this regard is the Montevideo Convention of 1933, which meticulously outlined the characteristics that define a sovereign state. According to this convention, a state must fulfill four fundamental benchmarks to be recognized as such: the presence of a permanent population, clearly defined territorial boundaries, a functioning government, and the capacity to enter into agreements with other states.

These criteria collectively form a comprehensive framework for evaluating the legitimacy of a newly formed state. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that the path to statehood is intricate, and the application of these criteria is not always a straightforward process. Numerous geopolitical, historical, and socio-economic factors can complicate the journey to independence for aspiring nations.
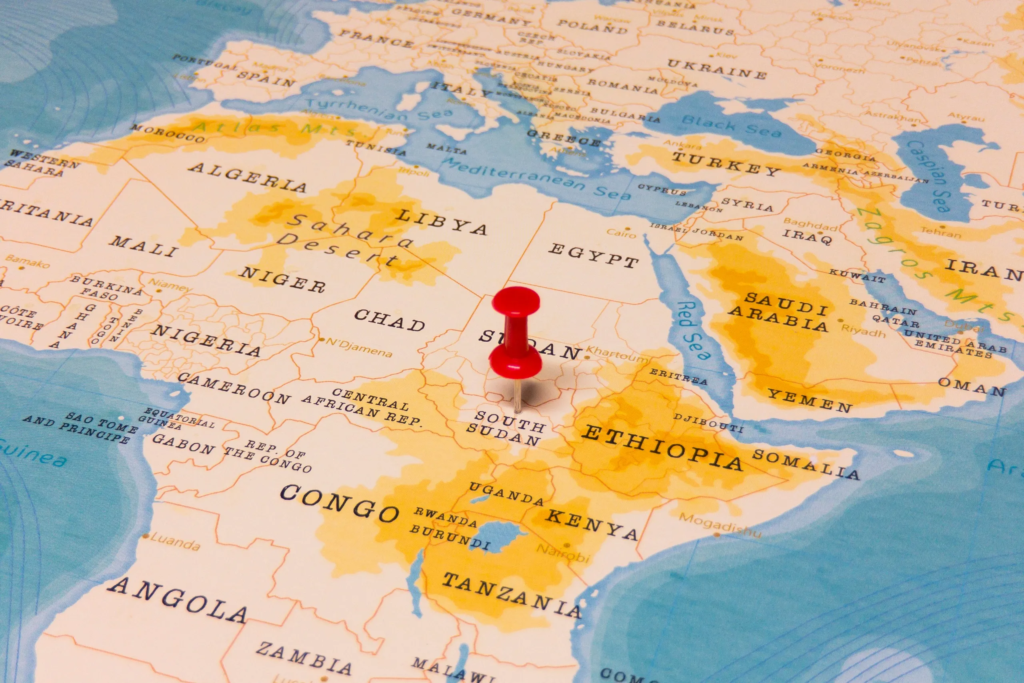
Self-determination and the United Nations
The newest country in the world : The concept of self-determination, encapsulating the right of a group to establish its own state and determine its political destiny, has been a fundamental principle embedded in various documents and declarations of the United Nations since the inception of its charter in 1945. While international law delineates criteria for achieving independence, securing widespread formal recognition is by no means assured. Numerous challenges can impede this process, ranging from resistance by the existing sovereign state to a dearth of acknowledgment from other nations.
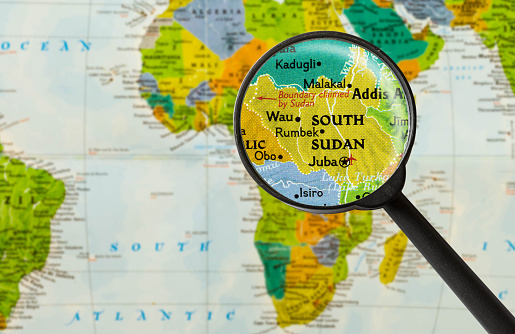
Such complexities have been starkly illustrated in the case of Kosovo, where despite meeting the criteria for statehood as per international law, the path to full recognition has been hindered by geopolitical considerations and differing perspectives on sovereignty. The journey toward formal acknowledgment of a new state involves navigating a complex web of diplomatic, political, and legal intricacies, underscoring the delicate balance between the aspirations of a people for self-determination and the complexities of international relations.
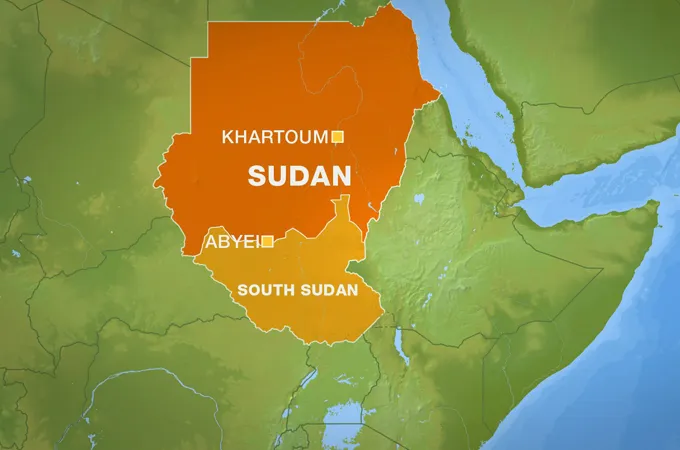
South Sudan’s path to independence
The newest country in the world : South Sudan’s journey to becoming the world’s newest country has roots in the complex history of Sudan. Originally the southern part of Sudan, which gained independence in 1956, South Sudan experienced marginalization due to diverse populations in the north and south. The predominantly Islamic north, with Arabic as the primary language, contrasted with the Christian and ethnically diverse south, where English became the language of education.

Two lengthy civil wars (1955–72 and 1983–2005) erupted due to tensions between the north and south. The Comprehensive Peace Agreement of 2005, supported by the international community, granted southern Sudan semiautonomous status and included provisions for a referendum on independence after six years. In January 2011, approximately 99 percent of voters chose secession in the referendum, leading to South Sudan’s formal declaration of independence later that year.

Conclusion
The creation of a new country involves complex historical, legal, and geopolitical factors. South Sudan’s path to independence reflects the challenges faced by regions seeking self-determination. While international law provides criteria for statehood, the actual process is influenced by various dynamics, including resistance from the existing country and the recognition of other nations. South Sudan’s successful journey to independence marks a significant moment in the ever-evolving landscape of international politics and statehood.
To explore more news : Click Here
ALSO READ : The Enigmatic And Fascinating Origins Of The Name “Europe”