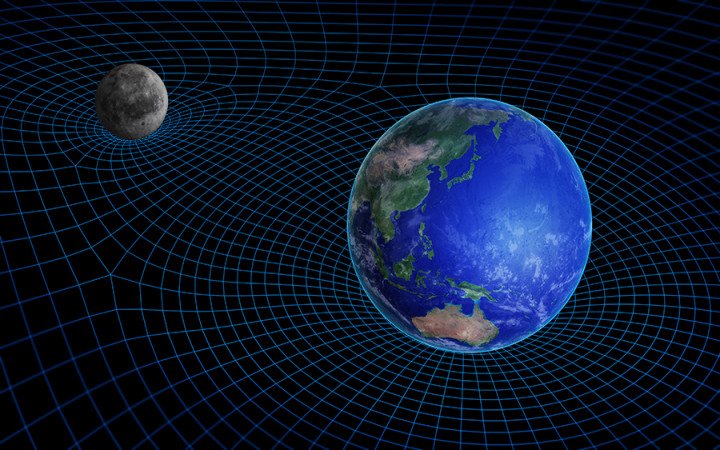
Space-time is the four-dimensional fabric of the universe, where space and time are intertwined and relative to each other. Space-time is the basis of Einstein’s theory of general relativity, which describes how gravity affects the shape and motion of space-time, and how space-time affects the movement and energy of matter and light. Space-time is also the arena of many fascinating phenomena, such as black holes, gravitational waves, and time dilation
space-time
However, space-time is not easy to visualize or comprehend, as it defies our common sense and intuition. We are used to thinking of space and time as separate and absolute entities, and we have difficulty imagining how they can bend, stretch, or warp. Moreover, we are limited by our three-dimensional perception and representation of reality, and we have trouble imagining how a fourth dimension can exist or look like
Fortunately, there is a mathematical trick that can help us imagine space-time, or at least get a glimpse of its nature and properties. This trick is called dimensional analogy, and it involves using lower-dimensional objects or spaces to illustrate or model higher-dimensional ones. For example, we can use a two-dimensional surface, such as a sheet of paper, to represent a three-dimensional space, such as a room. We can also use a one-dimensional line, such as a ruler, to represent a two-dimensional surface, such as a sheet of paper.
Also read : How The Existence Of Everything Could Soon Be Explained By New Research On Antimatter

Dimensional analogy can help us imagine space-time by using a two-dimensional surface to represent a four-dimensional space-time. For instance, we can use a rubber sheet to model the effect of gravity on space-time. We can place a heavy object, such as a ball, on the rubber sheet, and observe how it creates a dent or a curvature on the sheet. This dent represents how a massive object, such as a star or a planet, distorts the space-time around it. We can also roll a smaller object, such as a marble, on the rubber sheet, and observe how it follows a curved path around the dent. This path represents how a less massive object, such as a moon or a satellite, orbits the massive object, due to the curvature of space-time.
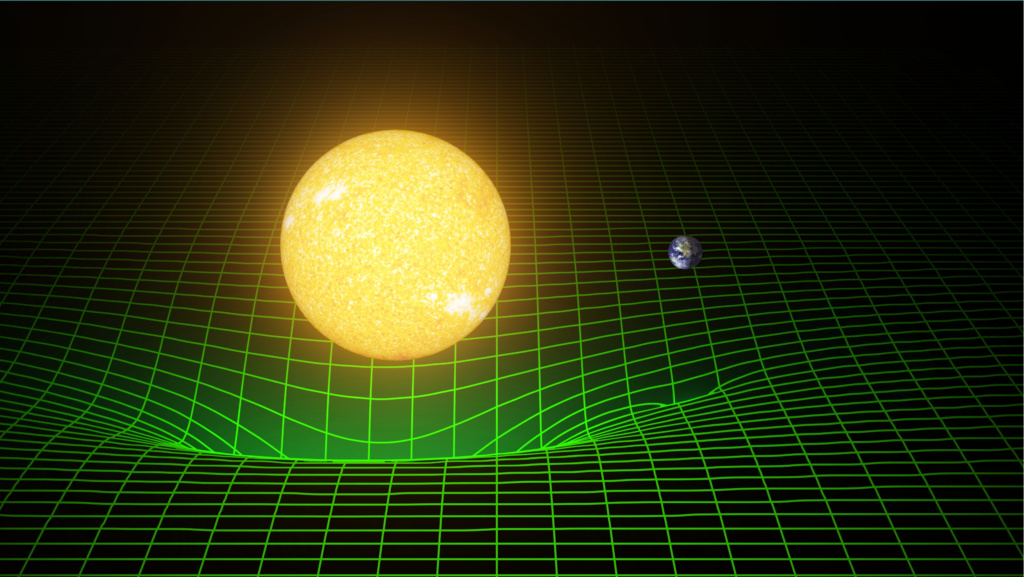
Another example of dimensional analogy is using a flat map to model the geometry of space-time. We can draw a grid of lines on the map, representing the coordinates of space and time. We can also draw a circle on the map, representing the circumference of the Earth. We can then measure the length of the circle and the length of the grid lines on the map, and compare them with the actual length of the circle and the grid lines on the Earth. We will find that the lengths on the map are distorted or stretched, depending on the projection or the method of mapping the Earth onto the map. This distortion represents how the geometry of space-time is affected by the presence of matter and energy, and how different observers may measure different lengths and angles in space-time.
These examples of dimensional analogy are not perfect or accurate representations of space-time, as they involve simplifications and approximations, and they may introduce errors or inconsistencies. However, they can serve as useful and intuitive tools to illustrate or demonstrate some of the basic concepts and principles of space-time, and to stimulate our imagination and curiosity.
FAQ: Use This Mathematical Method to Visualize Space-Time
Q: What mathematical method can be used to visualize space-time?
A: One powerful mathematical method used to visualize space-time is the creation of a “space-time diagram” or “light cone diagram.” This tool helps represent the relationships between space and time in a geometric format.
Q: How does a space-time diagram work?
A: A space-time diagram combines space and time on a two-dimensional plane, typically with time represented along the vertical axis and space along the horizontal axis. Events, objects, and the paths of light or other objects moving through space and time are depicted within this diagram.
Q: What is the significance of space-time diagrams in physics?
A: Space-time diagrams are essential in the field of physics, especially in the understanding of relativistic effects predicted by Einstein’s theory of general relativity. They visually illustrate how objects move through both space and time, providing insights into the curvature of space-time caused by massive objects.
Q: Can you explain the concept of a “light cone” in space-time diagrams?
A: A light cone represents the paths that light (or any other electromagnetic signals) emitted from a specific event can take through space and time. It consists of two parts: the “future light cone” and the “past light cone,” indicating the possible directions that light or information can travel.
Q: How are events and objects represented on a space-time diagram?
A: Events and objects are represented as points on the space-time diagram. The vertical position corresponds to the time of the event, and the horizontal position corresponds to the spatial location. Lines, or worldlines, depict the paths of objects through both space and time.
Q: Are space-time diagrams limited to theoretical physics?
A: While space-time diagrams are extensively used in theoretical physics, especially in relativity, they are valuable tools for anyone interested in visualizing the relationships between space and time. They provide an intuitive way to grasp complex concepts.
Q: Can space-time diagrams be created without advanced mathematical knowledge?
A: Basic space-time diagrams can be created without advanced mathematical knowledge. They involve graphing time and space on a coordinate system and plotting events or objects. However, a deeper understanding of the underlying physics may be required for more complex scenarios.
Q: Are there computer simulations or software for visualizing space-time?
A: Yes, various computer simulations and software tools are available for visualizing space-time. These tools allow for dynamic representations of complex interactions, aiding researchers and enthusiasts in exploring the effects of relativity.
Q: How does general relativity influence space-time diagrams?
A: General relativity predicts that massive objects, like planets or stars, can curve the fabric of space-time. Space-time diagrams illustrate this curvature, showing how objects with mass affect the paths of nearby objects and the geometry of space-time itself.
Also read : Dark Matter Detective Work: A Revolutionary Approach At The Large Hadron Collider




































