Explore All About Goods and Services Tax in this article : What Is GST ?, GST Full Form and GST 9
GST Full Form:
Goods and Services Tax is the full name of the GST. It was initially mentioned in the Budget Speech delivered on February 28, 2006. It set the stage for an extensive overhaul of India’s indirect tax system. Since its creation, the indirect taxation system has undergone a series of changes, and it was finally put into effect on July 1st, 2017, as the Goods and Services Tax Act.

ALSO READ : What Is Inclusion In Education : A Heartwarming Sneak Peek At Berlin’s Creative Model
Multiple indirect taxes that were imposed on various products and services were replaced by the Goods and Services Tax as a result of this tax reform. The regulatory agency in charge of overseeing all modifications to this tax is the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
What is GST (Goods and Services Tax)?
A value-added tax known as the Goods and Services Tax , which applies on the supply of goods and services for domestic use. Therefore, Goods and Services Tax is a comprehensive, single indirect tax law that applies to the entire nation.
The total cost of the goods includes this tax. When a consumer purchases the aforementioned item, the Goods and Services Tax is included in the price. The company or seller then sends the government their share of the Goods and Services Tax.
This tax is imposed by the Indian Central Government. This tax is split between the federal and state governments under CGST and SGST in the case of intrastate transactions.
Type Of Goods and Services Tax
On March 29, 2017, the Indian Parliament approved the Goods and Service Tax Act, which went into effect on July 1 of that same year. A variety of existing indirect taxes, including excise duty, VAT, service tax, etc., were replaced, and it was hailed as a landmark tax reform for the nation.

The Purpose Of Goods and Services Tax
- The elimination of various tax systems.
- Increased adherence to corporate rules.
- To lower the costs.
- Increase the total revenue of the nation.
- For increased productivity and efficiency.
The primary goals of Goods and Services Tax are:–
‘One Nation, One Tax’
Many previous indirect taxes were replaced by the Goods and Services Tax. ‘One Nation, One Tax’ was the main driving force for its introduction. It was created in this way to offer uniform tax rates for goods and services throughout all states. Even the administration of taxes and compliances was made simpler.
Indian indirect taxes to be absorbed
In India, the Goods and Services Tax was implemented in order to establish a centralized and uniform taxation system for goods and services. Most indirect taxes were combined into one under its legislation to make administration simpler.
Limiting Tax Evasion
Before the Goods and Services Tax was implemented, there was a significant amount of tax avoidance. Goods and Services Tax was implemented in India in order to reduce tax evasion and provide a centralized system of tax surveillance. It has significantly decreased the number of tax defaulters.
Goods and Services Tax was used to replace taxes:
- VAT
- Octroi
- Entertainment Tax
- Tax on Lottery
- Luxury Tax
- Purchase Tax
- Service Tax
- Additional Excise Duty
- Central Excise Duty and more.
Types of Goods and Services Tax :
The Goods and Services Tax ‘s organizational structure accounts for the type of transaction upon which the tax amount is assessed.
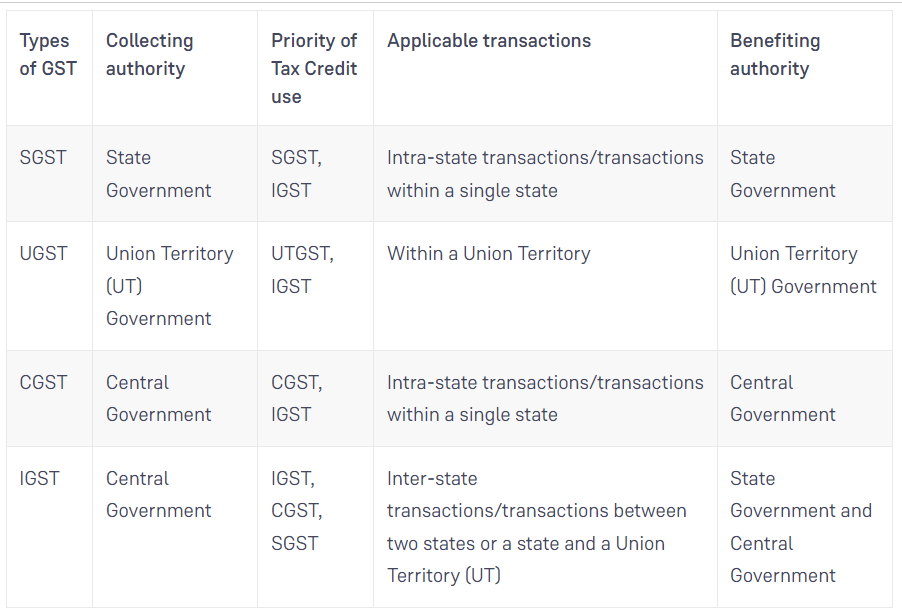
It is an exchange of money between two states. For instance, an iron ore supplier in Jharkhand sends iron ore to a customer in West Bengal. The Central government and the West Bengal government (State of consumption) split the Goods and Services Tax that was thusly collected.
An intra-state transaction is one that takes place inside of a State. As an illustration, a company in Jharkhand gives a customer in the State 1 tonne of iron ore. The Centre government and the Jharkhand government receive the Goods and Services Tax after that.

There are essentially three different types of Goods and Services Tax according on the nature of transactions:-
- State Goods and Services Tax or SGST
- Central Goods and Services Tax or CGST
- Integrated Goods and Services Tax or IGST

Who must pay the Goods and Services Tax?
Persons in the following groups are responsible for paying GST:
- GST-registered individuals who are engaged in taxable supply activities.
- People who are GST registered must make payments through the reverse charge procedure.
- Individuals who are obligated to withhold tax at source (TDS) under the GST.
- Operators of e-commerce who enrolled for GST.
- Operators of e-commerce who are GST-registered must collect tax at source (TCS).
- Individuals (agents) that provide goods or services on behalf of a manufacturer or supplier.

What is GSTR-9, and who is responsible for filing it?
It is an annual return to be filed by all registered taxpayers under GST irrespective of the turnover of an entity. The return includes information on inbound and outbound supplies, taxes paid, refunds claimed, demands made, and ITCs that the taxpayer was eligible to receive. Except for: All taxpayers who are registered must submit a GSTR-9.
- sporadic taxpayers
- Distribution Services for Input
- taxpaying non-residents
- Taxpayers who withhold or collect taxes at source in accordance with Section 51 or Section 52
If you want more details on it : Click Here
ALSO READ : The Best Books For Teenagers In 2023 To Empower Them : Let Them Conquer The World




































