A genetic condition known as hemophilia is brought on by a deficiency of specific proteins in the blood known as clotting factors. Among the co-occurring conditions that hemophiliacs frequently experience are
Intracranial hemorrhage: This refers to bleeding that occurs inside the skull, particularly into the brain or the surrounding tissues. Hemophilia’s acute consequences typically manifest as severe headaches, nausea, and convulsions, or even more abruptly after a head injury.

hemophilia
Development of Inhibitors: Inhibitors are antibodies that prevent clotting factors from working, particularly factor VIII in hemophilia A patients and factor IX in hemophilia B patients. A subset of people experience inhibitors, typically as a result of exogenous factor replacement therapy. By reducing the effectiveness of factor replacement therapy and raising the risk of bleeding problems, inhibitors complicate treatment and force physicians to consider alternate approaches like immunological tolerance induction therapy.
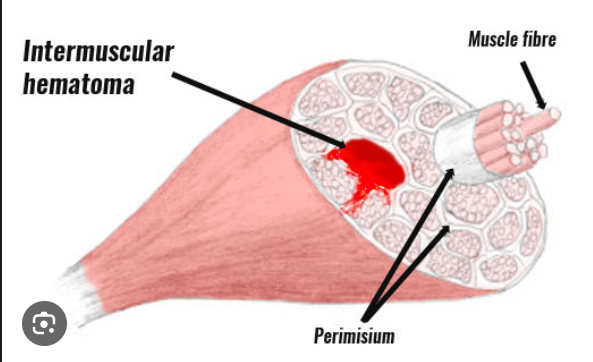
Hematomas in the Muscle: Hematomas are accumulations of blood in the muscle tissue that occur when hemophiliacs have severe bleeding. Areas of the affected muscle that are sensitive, swelling, and painful are observed in hematomas. Muscle hematomas are known to narrow the space surrounding surrounding nerves and tissues, leading to additional problems.
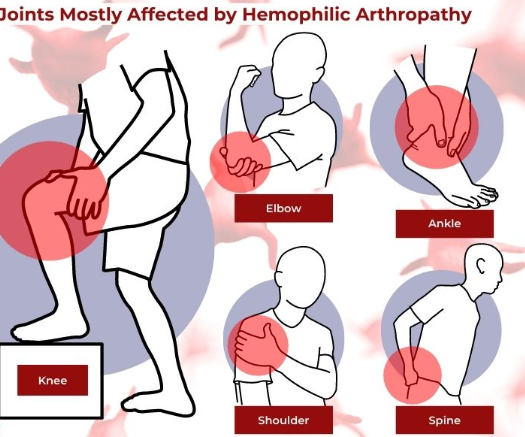
Hemophilic Arthropathy: Hemophilic arthropathy is characterized by persistent bleeding into the joints, which results in joint deterioration. It is well recognized that hemophilia mostly affects the elbows, ankles, and knees. Stiffness, discomfort, and edema are caused by bleeding in the joints. This lowers the quality of life and has a negative effect on mobility and physical movement. Hemophilic arthopathy sufferers require a variety of approaches to control and specifically care for their joints.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Individuals with hemophilia may experience bleeding in the digestive tract for a variety of reasons, including gastritis, gastrointestinal ulcers, and vascular anomalies. In these situations, people may experience symptoms like anemia, abdominal pain, and bloody stools. Depending on the underlying causes and extent of the bleeding, gastrointestinal hemorrhage can range from being minor to being lethal.

Treatment Complications: People with hemophilia frequently experience infections, allergies, and inhibitor development when undergoing treatment. These are frequently observed in patients receiving bypass medications or factor replacement therapy. When exposed to clotting factor concentrates, allergic reactions can manifest as anaphylaxis, hives, rash, itching, or wheezing.
Contributions from: Dr. Rahul Agrwal, Internal Medicine Consultant at CARE Hospitals in Hyderabad’s Hitech City
Also read: Yoga Positions To Help With Menopause Symptoms
images source: Google
Disclaimer: The opinions and suggestions expressed in this article are solely those of the individual analysts. These are not the opinions of HNN. For more, please consult with your doctor




































